Difference between revisions of "Virt-manager/en"
Views
Actions
Namespaces
Variants
Tools
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 19:07, 7 September 2021
Overview
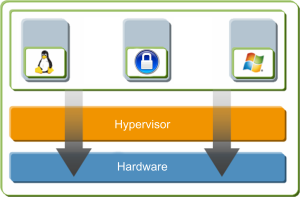
Virt-manager uses libvirt and it's a manager of many hypervisors, including the one that we want to use here: QEMU/KVM.
Why do I need to virtualize?
- To learn about a new O.S.
- To configure a hardware that has a setup only for that operating system
- To use a software that only works on another
I want to know more
1. Virtualization
2. Hypervisor
3. Virtual machine
What we absolutely must know
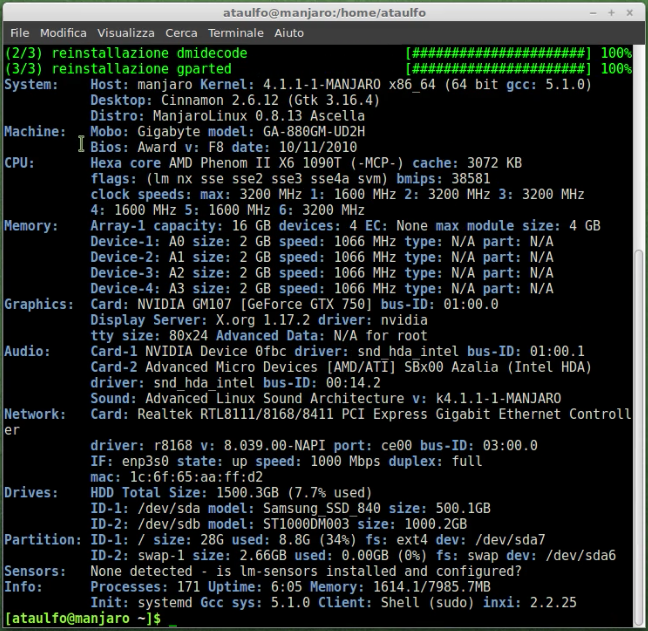
1. What is my CPU. Identify it and make sure it's at least a quad core. TAKE A LOOK AT CPU-World
2. Check if the 'virtualization parameters' are enabled on BIOS
3. How much memory I have. Check the RAM and verify that is at least 4GB.
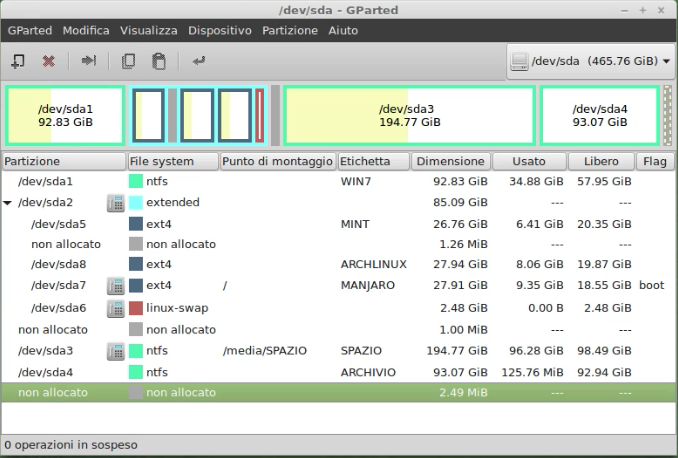
4. The amount of free space on my HDD.Launch gparted and make sure you have a partition with at least 20GB free. While you're there add a label to the partitions to better recognize them even by name.
5. The minimum hardware requirements of the operating system you want to install as a virtual machine.
From terminal:
sudo pacman -S inxi dmidecode gparted && sudo inxi -Fxm
Install virt-manager, qemu and all dependencies
From terminal:
sudo pacman -S virt-manager qemu vde2 ebtables dnsmasq bridge-utils openbsd-netcat
Enable and start service
sudo systemctl enable libvirtd.service sudo systemctl start libvirtd.service
Using Virt-Manager
1. Launch menu Virtual Machine Manager, check that it is connected.
2. Go to File, choose Add Connection and choose hypervisor QEMU/KVM user session. Click on connect.From the screen select the first qemu / kvm, Right click, disconnect and delete it.
3. You need the HDD space in which to create the virtual machine and copy the ISO file of the operating system (but you can also use a burned cd/dvd ). Double click qemu/kvm, go on storage and add by clicking + the path to the folder where you have the iso and the folder where create the virtual machine.
4. Click on create a new virtual machine: select cdrom or iso (first path maked to put the iso file)
5. How many CPU assign and how much memory? (check the recommended requirements of O.S. that you are installing)
6. Create the file system of the virtual machine by selecting managed or other storage and create the volume of the virtual machine. How many GB? Check the recommended requirements O.S. you install.
7.Assign a name to the machine and flag customize before installing. You have access to the screen with all the hardware that will be virtualized, do a check if there is all that is needed to initialize and launch the installer.
8. Click on the top to start.
Install guest additions
Once the VM is started and running you have to install the guest spice tools.
For Windows is a single package: spice-guest-tools-xxxx.exe
For linux are: spice-vdagent and xf86-video-qxl. If you visrtualize a linux distro you can install them with their package manager
Visit: Spice download