Difference between revisions of "Virt-manager"
Views
Actions
Namespaces
Variants
Tools
m (added languages and translate tags) |
m (Using the verb rather than the noun) |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
<translate> | <translate> | ||
= Overview = | = Overview = <!--T:1--> | ||
<!--T:2--> | |||
[[file:topbar_logo.png|left]] | [[file:topbar_logo.png|left]] | ||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
{{tip|Have you heard about Virtualbox to virtualize operating systems like Linux and Windows or Mac? It 'a good software, but not the only one! Don't forget VMware, Gnome Boxes and ...virt-manager. }} | {{BoxSuccess|tip|Have you heard about Virtualbox to virtualize operating systems like Linux and Windows or Mac? It 'a good software, but not the only one! Don't forget VMware, Gnome Boxes and ...virt-manager. }} | ||
<!--T:3--> | |||
---- | ---- | ||
'''[https://virt-manager.org/ Virt-manager]''' uses '''[http://libvirt.org/ libvirt]''' and it's a manager of many hypervisors, including the one that we want to use here: QEMU/KVM. | <!--T:4--> | ||
'''[https://virt-manager.org/ Virt-manager]''' uses '''[http://libvirt.org/ libvirt]''' and it's a manager of many '''[https://libvirt.org/drivers.html hypervisors]''', including the one that we want to use here: QEMU/KVM. | |||
<!--T:5--> | |||
---- | ---- | ||
<!--T:6--> | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
<!--T:7--> | |||
'''Why do I need to virtualize?''' | '''Why do I need to virtualize?''' | ||
<!--T:8--> | |||
* To learn about a new O.S. | * To learn about a new O.S. | ||
<!--T:9--> | |||
* To configure a hardware that has a setup only for that operating system | * To configure a hardware that has a setup only for that operating system | ||
<!--T:10--> | |||
* To use a software that only works on another | * To use a software that only works on another | ||
= I want to know more = | = I want to know more = <!--T:11--> | ||
<!--T:12--> | |||
[[file:Hypervisor_1.png|left]] | [[file:Hypervisor_1.png|left]] | ||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 46: | ||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
= What we absolutely must know = | = What we absolutely must know = <!--T:13--> | ||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
1. What is my CPU. Identify it and make sure it's at least a quad core. '''TAKE A LOOK AT''' '''[http://www.cpu-world.com/CPUs/CPU.html CPU-World]''' | 1. What is my CPU. Identify it and make sure it's at least a quad core. '''TAKE A LOOK AT''' '''[http://www.cpu-world.com/CPUs/CPU.html CPU-World]''' | ||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
2. Check if the 'virtualization parameters' are enabled on BIOS | 2. Check if the 'virtualization parameters' are enabled on BIOS using | ||
{{UserCmd|command=LC_ALL=C lscpu | grep Virtualization}} | |||
3. How much memory I have. Check the RAM and verify that is at least 4GB. | 3. How much memory I have. Check the RAM and verify that is at least 4GB. | ||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
4. The amount of free space on my | 4. The amount of free space on my hard drive. The virtual machine can use a disk image file so extra partitions are not necessary. | ||
{{note|You can also use raw partition specific for virtual machines. See [https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/Partitioning partitioning] for more information}} | |||
5. The minimum hardware requirements of the operating system you want to install as a virtual machine. | 5. The minimum hardware requirements of the operating system you want to install as a virtual machine. | ||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
= Install virt-manager, qemu and all dependencies= <!--T:16--> | |||
<br clear="all" /> | |||
From terminal: | From terminal: | ||
{{UserCmd|command=sudo pacman -S --needed virt-manager qemu-desktop libvirt edk2-ovmf dnsmasq iptables-nft}} | |||
For TPM support: | |||
{{UserCmd|command=sudo pacman -S --asdeps swtpm}} | |||
Enable and start service | |||
{{UserCmd|command=sudo systemctl enable libvirtd.service}} | |||
Add user to ''libvirt,'' ''libvirt-qemu'' and ''kvm'' groups to use the '''system'''-level virtual machines (qemu:///system). | |||
{{UserCmd|command=sudo usermod -a -G libvirt,libvirt-qemu,kvm $USER}} | |||
Note that you will need to restart userspace for the groups to become active. To restart userspace | |||
{{UserCmd|command=systemctl soft-reboot}} | |||
{{note| | |||
# You don't need this step to run system-level virtual machines. However, virt-manager will prompt for sudoer's password when launch if the user is not in the ''libvirt'' group | |||
# You can also create '''user'''-level virtual machines (qemu:///session) and use without sudoer's privelige. However, some features such as [https://libvirt.org/kbase/virtiofs.html VirtioFS file sharing] may be unavailable in qemu:///session}} | |||
[[ | = Using Virt-Manager for guest creation= <!--T:17--> | ||
< | |||
<!--T:25--> | |||
0. Prepare installation image. If you're going to install Windows, prepare the [https://www.linux-kvm.org/page/WindowsGuestDrivers/Download_Drivers Virtio driver] image too. | |||
{{tip|You can also find the [https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/virtio-win virtio-win] package in AUR. The image is located in '''/var/lib/libvirt/images''', which is the default [https://libvirt.org/storage.html#StorageBackendDir directory pool] of qemu:///system}} | |||
<!--T:26--> | |||
1. Launch menu Virtual Machine Manager. It should already have a [https://libvirt.org/drvlxc.html LXC] connection. You can disconnect and remove it if you don't use LXC. | |||
<!--T:27--> | |||
2. Go to File, choose Add Connection and choose hypervisor QEMU/KVM, or QEMU/KVM user session if you don't want '''system'''-level virtual machines. Click on connect. | |||
<!--T:28--> | |||
3. You need directory pools to store the disk images of virtual machines or the ISO file of CD/DVD. Double click qemu/kvm, go on storage and add by clicking + the path to the folder where you have the iso and the folder where create the virtual machine. | |||
<!--T:29--> | |||
{{BoxInfo|tip|Advice: use a different partition than the root. In case you need to reinstall your operating system you don't lose the VM that already ready-to-start.}} | |||
4. Click on create a new virtual machine: select '''Local install media (ISO image or CDROM)''', and select the installation ISO image and OS type (if not detected). | |||
<!--T:30--> | |||
5. How many CPU assign and how much memory? (check the recommended requirements of O.S. that you are installing) | 5. How many CPU assign and how much memory? (check the recommended requirements of O.S. that you are installing) | ||
<!--T:31--> | |||
6. Create the file system of the virtual machine by selecting '''Select or create custom storage''' and click '''Manage...'''. Under your desired directory pool, create the volume of the virtual machine (default in qcow2 format). How many GB? Check the recommended requirements O.S. you install. | |||
<!--T:32--> | |||
7.Assign a name to the machine and flag '''customize configuration before install'''. You have access to the screen with all the hardware that will be virtualized, do a check if there is all that is needed to initialize and launch the installer. | |||
<!--T:33--> | |||
8. In ''Overview'', change the firmware to UEFI for future-proof capacity. | |||
<!--T:34--> | |||
9. Change the type of SATA Disk 1 (the disk image of the creating virtual machine) to ''virtio'' for better performance. Change discard mode to ''unmap'', and then apply the change. You should notice the device name would change from SATA Disk 1 to VirtIO Disk 1. | |||
{{BoxWarning|Warning|If you're installing Windows, make sure to create a new SATA CDROM device and select the '''virtio-win''' image as the media, so that the Windows Installer can load the driver to recognize the disk. The virtio storage driver should be located at somewhere like ''E:\viostor\w10\amd64''}} | |||
10. Set the NIC type to virtio too for better network performance. | |||
{{BoxInfo|Note|If you're installing Windows, once the system if ready, make sure to install all the virtio drivers so that your virtIO network can work normally}} | |||
11. Add TPM chip, select '''TIS''' model through '''Emulated device''' backend. | |||
<!--T:35--> | |||
12. Add a watchdog to reboot the guest when it hangs. Leave the settings as default. | |||
<!--T:36--> | |||
13. And a hardware RNG, to get entropy from the host. | |||
<!--T:37--> | |||
14. Click on the top to start installation. | |||
<!--T:38--> | |||
{{BoxWarning|Warning|'''All these steps are visible on youtube.''' '''[https://youtu.be/DiUG_hlLk3c >>> PLAY THIS] [[File:YouTube_1.png|thumb|center|300px]]'''}} | |||
==Install guest additions== <!--T:21--> | |||
Once the VM is started and running you have to install the [https://www.spice-space.org/download.html spice guest tools]. | |||
<!--T:39--> | |||
For Windows is a single package: spice-guest-tools-xxxx.exe | |||
<!--T:40--> | |||
For linux are: spice-vdagent and xf86-video-qxl. If you visrtualize a linux distro you can install them with their package manager | |||
<!--T:41--> | |||
Visit: '''[http://www.spice-space.org/download.html Spice download]''' | |||
==Tune the display settings== <!--T:22--> | |||
The default model of display card is QXL. If your virtual machine is Linux system, you can change it to virtio and enable 3D acceleration for better graphic performance. | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
Windows virtual machine, however doesn't support virtio display yet. Nevertheless, we can increase its VGA memory from the default 16 MB to 64 MB to allow higher display resolution and slightly better 2D graphical performance. | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
To do so, we need to edit the XML file of the virtual machine. | |||
# In virt-manager, go to edit > preference, and check '''Enable XML edit'''. | |||
# In virtual machine details, go to display card. Under the XML tab, change the value of '''vgamem''' to 65536, then apply the change. | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
==File sharing between host and guest== <!--T:23--> | |||
For Linux guests, Virtio-FS and 9p are available for file sharing. See [https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/Libvirt#Sharing_data_between_host_and_guest ArchWiki] for more information. | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
For Windows guest, the easiest way to share file between host and guest is through [https://wiki.manjaro.org/index.php/Using_Samba_in_your_File_Manager SAMBA]. | |||
# Create a SAMBA usershare | |||
# In Windows guest, enter '''\\192.168.122.1''' in the file explorer, and you should be able to see the usershare on your host. | |||
# Map that SAMBA usershare to a new drive, and connect to it with the appropriate credential. That's it. | |||
Check [https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/configuring_and_managing_virtualization/sharing-files-between-the-host-and-its-virtual-machines_configuring-and-managing-virtualization#sharing-files-between-the-host-and-windows-virtual-machines_sharing-files-between-the-host-and-its-virtual-machines this article] for more information. | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
==Optimize vCPU== <!--T:24--> | |||
Check [https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/Fedora/13/html/Virtualization_Guide/ch25s06.html this article] to customize vCPU topology for better performance. | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
For | For example, my CPU has 1 socket, 8 cores, and 16 threads in total. The automatic topology assigns 4 sockets, 1 core, and 1 thread to my guest. After changing it to 1 socket, 4 cores, and 1 thread, the performance increases significantly. | ||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
= References = | =Lab: Windows 11= <!--T:42--> | ||
Windows Setup provides for setting up virtual Windows system for lab purpose. It can be for testing software or for pentesting. | |||
<!--T:43--> | |||
For a continued use of Windows you will need a valid license key to run a virtualized Windows. | |||
==Prepare== <!--T:44--> | |||
<!--T:45--> | |||
* Create a new virtual machine | |||
* Select a Windows 11 ISO file | |||
* Accept the defaults clicking Next until you reach the final screen | |||
* Tick the box Customize configuration before install and click Finish | |||
* In the Overview pane - set vm firmware to BIOS and click Apply | |||
* Click the button Begin Installation | |||
==Install== <!--T:46--> | |||
<!--T:47--> | |||
Before starting the installer press ShiftF10 so launch the Windows Cmd utility and launch regedit. | |||
<!--T:48--> | |||
* Expand HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\Setup | |||
* Add new key named LabConfig | |||
* Add new DWORD value with name BypassTPMCheck and change the value to 1. | |||
* Add new DWORD value with name BypassRAMCheck and change the value to 1. | |||
* Add new DWORD value with name BypassSecureBootCheck and change the value to 1. | |||
<!--T:49--> | |||
Close the registry editor and exit the shell, then continue the installer | |||
==Final Setup== <!--T:50--> | |||
During last stage the installer will insist in network access but you may want use a local account instead of the required Microsoft account. | |||
<!--T:51--> | |||
This can be disabled using the Cmd utility ShiftF10 | |||
<!--T:53--> | |||
* enter OOBE\BYPASSNRO and press Enter | |||
* close the Cmd utility | |||
* back in the setup window click I don't have internet | |||
= References = <!--T:18--> | |||
<!--T:19--> | |||
'''[https://virt-manager.org/ Virt-manager]''' | '''[https://virt-manager.org/ Virt-manager]''' | ||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:33, 1 November 2024
Overview
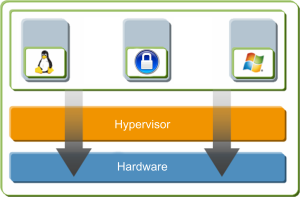
Virt-manager uses libvirt and it's a manager of many hypervisors, including the one that we want to use here: QEMU/KVM.
Why do I need to virtualize?
- To learn about a new O.S.
- To configure a hardware that has a setup only for that operating system
- To use a software that only works on another
I want to know more
1. Virtualization
2. Hypervisor
3. Virtual machine
What we absolutely must know
1. What is my CPU. Identify it and make sure it's at least a quad core. TAKE A LOOK AT CPU-World
2. Check if the 'virtualization parameters' are enabled on BIOS using
3. How much memory I have. Check the RAM and verify that is at least 4GB.
4. The amount of free space on my hard drive. The virtual machine can use a disk image file so extra partitions are not necessary.
5. The minimum hardware requirements of the operating system you want to install as a virtual machine.
Install virt-manager, qemu and all dependencies
From terminal:
For TPM support:
Enable and start service
Add user to libvirt, libvirt-qemu and kvm groups to use the system-level virtual machines (qemu:///system).
Note that you will need to restart userspace for the groups to become active. To restart userspace
Using Virt-Manager for guest creation
0. Prepare installation image. If you're going to install Windows, prepare the Virtio driver image too.
1. Launch menu Virtual Machine Manager. It should already have a LXC connection. You can disconnect and remove it if you don't use LXC.
2. Go to File, choose Add Connection and choose hypervisor QEMU/KVM, or QEMU/KVM user session if you don't want system-level virtual machines. Click on connect.
3. You need directory pools to store the disk images of virtual machines or the ISO file of CD/DVD. Double click qemu/kvm, go on storage and add by clicking + the path to the folder where you have the iso and the folder where create the virtual machine.
4. Click on create a new virtual machine: select Local install media (ISO image or CDROM), and select the installation ISO image and OS type (if not detected).
5. How many CPU assign and how much memory? (check the recommended requirements of O.S. that you are installing)
6. Create the file system of the virtual machine by selecting Select or create custom storage and click Manage.... Under your desired directory pool, create the volume of the virtual machine (default in qcow2 format). How many GB? Check the recommended requirements O.S. you install.
7.Assign a name to the machine and flag customize configuration before install. You have access to the screen with all the hardware that will be virtualized, do a check if there is all that is needed to initialize and launch the installer.
8. In Overview, change the firmware to UEFI for future-proof capacity.
9. Change the type of SATA Disk 1 (the disk image of the creating virtual machine) to virtio for better performance. Change discard mode to unmap, and then apply the change. You should notice the device name would change from SATA Disk 1 to VirtIO Disk 1.
10. Set the NIC type to virtio too for better network performance.
11. Add TPM chip, select TIS model through Emulated device backend.
12. Add a watchdog to reboot the guest when it hangs. Leave the settings as default.
13. And a hardware RNG, to get entropy from the host.
14. Click on the top to start installation.
Install guest additions
Once the VM is started and running you have to install the spice guest tools.
For Windows is a single package: spice-guest-tools-xxxx.exe
For linux are: spice-vdagent and xf86-video-qxl. If you visrtualize a linux distro you can install them with their package manager
Visit: Spice download
Tune the display settings
The default model of display card is QXL. If your virtual machine is Linux system, you can change it to virtio and enable 3D acceleration for better graphic performance.
Windows virtual machine, however doesn't support virtio display yet. Nevertheless, we can increase its VGA memory from the default 16 MB to 64 MB to allow higher display resolution and slightly better 2D graphical performance.
To do so, we need to edit the XML file of the virtual machine.
- In virt-manager, go to edit > preference, and check Enable XML edit.
- In virtual machine details, go to display card. Under the XML tab, change the value of vgamem to 65536, then apply the change.
File sharing between host and guest
For Linux guests, Virtio-FS and 9p are available for file sharing. See ArchWiki for more information.
For Windows guest, the easiest way to share file between host and guest is through SAMBA.
- Create a SAMBA usershare
- In Windows guest, enter \\192.168.122.1 in the file explorer, and you should be able to see the usershare on your host.
- Map that SAMBA usershare to a new drive, and connect to it with the appropriate credential. That's it.
Check this article for more information.
Optimize vCPU
Check this article to customize vCPU topology for better performance.
For example, my CPU has 1 socket, 8 cores, and 16 threads in total. The automatic topology assigns 4 sockets, 1 core, and 1 thread to my guest. After changing it to 1 socket, 4 cores, and 1 thread, the performance increases significantly.
Lab: Windows 11
Windows Setup provides for setting up virtual Windows system for lab purpose. It can be for testing software or for pentesting.
For a continued use of Windows you will need a valid license key to run a virtualized Windows.
Prepare
- Create a new virtual machine
- Select a Windows 11 ISO file
- Accept the defaults clicking Next until you reach the final screen
- Tick the box Customize configuration before install and click Finish
- In the Overview pane - set vm firmware to BIOS and click Apply
- Click the button Begin Installation
Install
Before starting the installer press ShiftF10 so launch the Windows Cmd utility and launch regedit.
- Expand HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\Setup
- Add new key named LabConfig
- Add new DWORD value with name BypassTPMCheck and change the value to 1.
- Add new DWORD value with name BypassRAMCheck and change the value to 1.
- Add new DWORD value with name BypassSecureBootCheck and change the value to 1.
Close the registry editor and exit the shell, then continue the installer
Final Setup
During last stage the installer will insist in network access but you may want use a local account instead of the required Microsoft account.
This can be disabled using the Cmd utility ShiftF10
- enter OOBE\BYPASSNRO and press Enter
- close the Cmd utility
- back in the setup window click I don't have internet