Difference between revisions of "Install Desktop Environments"
Views
Actions
Namespaces
Variants
Tools
imported>Ringo32 (→KDE) |
(Marked this version for translation) |
||
| (76 intermediate revisions by 16 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages/> | |||
__TOC__ | |||
= | <translate> | ||
= Overview = <!--T:1--> | |||
<!--T:2--> | |||
There are several desktop environments and window managers available for Manjaro, each with their own unique style, interface, and features. Furthermore, it is possible to install multiple environments if desired, which can be selected at the login screen at any time. Users are not restricted to whatever comes pre-installed with a particular flavour of Manjaro. | |||
= Desktop Environments = <!--T:3--> | |||
<!--T:4--> | |||
It is worth noting that a desktop environment (DE) is not a single entity; it is actually a collection of different components that work together. This commonly includes a: | |||
<!--T:5--> | |||
* '''window manager''' to display, move and resize application windows | * '''window manager''' to display, move and resize application windows | ||
* '''file manager''' to visually browse, copy and access files, etc. | * '''file manager''' to visually browse, copy and access files, etc. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 24: | ||
And so on. Most desktop environments will also come with their own preferred applications, in addition to various widgets, addons, and extensions to provide extra features. As such, upon entering the commands provided below in your terminal to download and install a desktop environment, you may be prompted to choose from a selection of components provided for it. '''To install a full desktop environment''' - complete with its own preferred file manager, applications, and so on | <!--T:6--> | ||
And so on. Most desktop environments will also come with their own preferred applications, in addition to various widgets, addons, and extensions to provide extra features. As such, upon entering the commands provided below in your terminal to download and install a desktop environment, you may be prompted to choose from a selection of components provided for it. '''To install a full desktop environment''' - complete with its own preferred file manager, applications, and so on | |||
<!--T:7--> | |||
Where additional (and optional) extras for a desktop environment are available, the terminal commands to obtain these have also been provided. | |||
<!--T:8--> | |||
Some important information about installing the Manjaro settings packages: | |||
* The Manjaro settings packages contain the theming and settings to make the desktop the same as in the Manjaro ISOs | |||
* They have the naming convention manjaro-<desktop>-settings i.e. manjaro-xfce-settings | |||
* They share files so you can only have one at a time installed. | |||
* If you are coming from gnome you must remove the meta package '''manjaro-gnome-assets''' before you can install the settings package for another desktop | |||
==The Risks of Using Multiple DEs== <!--T:9--> | |||
<!--T:10--> | |||
Installing multiple DEs is not without risks. Here are some things that can pop-up when running more than one DE: | |||
* The settings packages overlap so you can only have one DE pre-configured with the Manjaro theming. The others will need to have the theming applied manually. | |||
* You can end up with more than one instance of similar applications. For example, it is common to end up with 2 Bluetooth managers. It takes some tweaking to get a single manager working in multiple DEs. | |||
* Sometimes two different DEs will share the same configuration files causing strange things to happen, especially with theming. | |||
<!--T:11--> | |||
These risks are greatly reduced by using a different user account for each DE. | |||
<!--T:12--> | |||
In summary, running multiple DEs is possible and a great way to enjoy Manjaro but it requires a willingness to troubleshoot and work through minor problems. If you are the type of person who wants everything to "just work" out of the box, running multiple DEs might not be for you. | |||
== Xfce == <!--T:13--> | |||
<!--T:14--> | |||
[[File: xfceDE.png|thumb|left|375px]] | [[File: xfceDE.png|thumb|left|375px]] | ||
'''[http://xfce.org/ XFCE | <!--T:15--> | ||
'''[http://xfce.org/ Xfce]''' or '''XFCE''', pronounced as four individual letters, is a lightweight and versatile desktop environment that utilises a classic drop-down/pop-up menu to access applications. It is also compatible with '''[[Compiz_and_Emerald|Compiz]]'''. A little time and effort will also be required to properly customise the desktop to suit personal taste. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running Xfce uses about 390MB of memory. As of version 18, Manjaro has moved to the gtk3 version of Xfce. | |||
====== Install a basic Xfce environment ====== <!--T:16--> | |||
<!--T:17--> | |||
sudo pacman -S xfce4 xfce4-goodies xfce4-terminal network-manager-applet xfce4-notifyd xfce4-whiskermenu-plugin tumbler engrampa | |||
====== Optional: Install and use LightDM, the recommended display manager for Xfce ====== <!--T:18--> | |||
sudo pacman -S lightdm lightdm-gtk-greeter lightdm-gtk-greeter-settings | |||
sudo systemctl enable lightdm.service --force | |||
edit '''/etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf''', under [Seat:*] replace the greeter-session setting with '''greeter-session=lightdm-gtk-greeter''' | |||
====== Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for Xfce ====== <!--T:19--> | |||
sudo pacman -S manjaro-xfce-settings manjaro-settings-manager | |||
<!--T:20--> | |||
To configure LightDM to match the official iso replace the contents of /etc/lightdm/lightdm-gtk-greeter.conf with | |||
[greeter] | |||
background = /usr/share/backgrounds/illyria-default-lockscreen.jpg | |||
font-name = Cantarell Bold 12 | |||
xft-antialias = true | |||
icon-theme-name = Papirus | |||
screensaver-timeout = 60 | |||
theme-name = Matcha-azul | |||
cursor-theme-name = xcursor-breeze | |||
show-clock = false | |||
default-user-image = #avatar-default | |||
xft-hintstyle = hintfull | |||
position = 50%,center 50%,center | |||
clock-format = | |||
panel-position = bottom | |||
indicators = ~host;~spacer;~clock;~spacer;~language;~session;~a11y;~power | |||
====== Create a new user for the new desktop environment ====== <!--T:21--> | |||
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> | |||
sudo passwd <username> | |||
<!--T:22--> | |||
<br clear="all" /> | |||
== KDE Plasma 6 == <!--T:23--> | |||
[[File: KDEPlasmaDE.png|thumb|left|375px]] | |||
<!--T:24--> | |||
'''[http://www.kde.org/ The KDE community]''' offers [https://www.kde.org/plasma-desktop Plasma], a feature-rich and versatile desktop environment that provides several different styles of menu to access applications. An excellent built-in interface to easily access and install new themes, widgets, etc, from the internet is also worth mentioning. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running KDE uses about 455MB of memory. | |||
<!--T:159--> | |||
{{warning|The various components for Plasma which is available using the internet, should be used with care. Theming on Plasma is not just a bunch of icons and colors - it is based on QML, the Qt model language which is specific for the used version of Qt.}} | |||
====== Install a basic KDE Plasma environment ====== <!--T:25--> | |||
<!--T:26--> | |||
sudo pacman -S plasma kio-extras | |||
====== Optional: Install KDE applications ====== <!--T:27--> | |||
<!--T:28--> | |||
To install a full set of K* applications use '''kde-applications-meta'''. This will be ~300 packages(including dependencies) | |||
sudo pacman -S kde-applications-meta | |||
====== Optional: Install and use [https://wiki.manjaro.org/index.php?title=Install_Display_Managers#SDDM SDDM], the recommended display manager for KDE ====== <!--T:29--> | |||
<!--T:30--> | |||
SDDM is installed as a dependency of plasma. To enable it | |||
systemctl enable sddm.service --force | |||
systemctl reboot | |||
====== Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for plasma ====== <!--T:31--> | |||
sudo pacman -S manjaro-kde-settings sddm-breath-theme manjaro-settings-manager | |||
<!--T:32--> | |||
Open plasma settings, go to Startup & Shutdown->Login Screen and select "Breath" | |||
<!--T:33--> | |||
Alternatively, the newer themes may be installed with: | |||
sudo pacman -S | <!--T:34--> | ||
sudo pacman -S plasmat-themes-breath | |||
====== Create a new user for the new desktop environment ====== <!--T:35--> | |||
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,wheel <username> | |||
sudo passwd <username> | |||
<!--T:36--> | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
== | == GNOME 3 == <!--T:37--> | ||
[[File: Gnome-de-18.jpg|thumb|left|375px]] | |||
<!--T:38--> | |||
'''[http://www.gnome.org/ GNOME 3]''' is an intuitive desktop environment that utilises a tablet or smartphone style interface to access applications. It is not compatible with compiz. Although GNOME is very easy to learn and use, it has limited customisation options and it can be difficult to configure. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running GNOME uses about 447MB of memory. | |||
====== Install a basic GNOME environment ====== <!--T:39--> | |||
<!--T:40--> | |||
sudo pacman -S gnome | |||
====== Optional: To install extra themes, games, and features ====== <!--T:41--> | |||
<!--T:42--> | |||
sudo pacman -S gnome-extra | |||
====== Optional: Install and use GDM, the recommended display manager for GNOME ====== <!--T:43--> | |||
<!--T:44--> | |||
GDM is installed as a dependency of GNOME. To enable it: | |||
systemctl enable gdm.service --force | |||
====== Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for GNOME ====== <!--T:45--> | |||
sudo pacman -S manjaro-gnome-settings manjaro-settings-manager | |||
====== Create a new user for the new desktop environment ====== <!--T:46--> | |||
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> | |||
sudo passwd <username> | |||
<!--T:47--> | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
== | == Budgie == <!--T:48--> | ||
[[File: budgie.jpg|thumb|left|375px]] | |||
[ | <!--T:49--> | ||
The '''[https://github.com/BuddiesOfBudgie/budgie-desktop Budgie Desktop]''' is a modern desktop designed to keep out the way of the user. It features heavy integration with the GNOME stack in order for an enhanced experience. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running Budgie uses about 632MB of memory. | |||
====== Install a basic Budgie environment ====== <!--T:50--> | |||
<!--T:51--> | |||
sudo pacman -S budgie-desktop network-manager-applet gnome-control-center gnome-screensaver | |||
sudo pacman -S gnome | ====== Optional: Install additional commonly used components ====== <!--T:52--> | ||
sudo pacman -S gnome-terminal nautilus budgie-extras dconf-editor | |||
====== Optional: Install and use LightDM, the recommended display manager for budgie ====== <!--T:53--> | |||
sudo pacman -S lightdm lightdm-slick-greeter lightdm-settings | |||
systemctl enable lightdm.service --force | |||
edit ''/etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf'', under '''[Seat:*]''' replace the greeter-session setting with '''greeter-session=lightdm-slick-greeter''' | |||
sudo pacman -S | ====== Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for Budgie ====== <!--T:54--> | ||
sudo pacman -S manjaro-budgie-settings manjaro-settings-manager papirus-maia-icon-theme | |||
<!--T:55--> | |||
To configure LightDM to match the official iso replace the contents of /etc/lightdm/slick-greeter.conf with | |||
[Greeter] | |||
background=/usr/share/backgrounds/manjaro-budgie/manjaro-budgie.jpg | |||
theme-name=Matcha-sea | |||
icon-theme-name=Papirus-Maia | |||
draw-grid=false | |||
====== Create a new user for the new desktop environment ====== <!--T:56--> | |||
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> | |||
sudo passwd <username> | |||
<!--T:57--> | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
== Cinnamon == | == Cinnamon == <!--T:58--> | ||
[[File: Cinnamon screenshot.jpeg|thumb|left|375px]] | |||
<!--T:59--> | |||
'''[http://cinnamon.linuxmint.com/ Cinnamon]''' is a desktop environment based on GNOME 3 that utilises a large panel-style menu to access applications. It is not compatible with compiz. Despite being based on GNOME, it has more customisation options and therefore is easier to configure. Windows Vista or 7 users may find Cinnamon's interface comfortably familiar. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running Cinnamon uses about 665MB of memory. | |||
====== Install a basic Cinnamon environment ====== <!--T:60--> | |||
<!--T:61--> | |||
sudo pacman -S cinnamon | |||
====== Optional: Install additional commonly used components ====== <!--T:62--> | |||
sudo pacman -S cinnamon-wallpapers cinnamon-sounds gnome-terminal parcellite | |||
====== Optional: Install and use LightDM, the recommended display manager for cinnamon ====== <!--T:63--> | |||
sudo pacman -S lightdm lightdm-slick-greeter lightdm-settings | |||
systemctl enable lightdm.service --force | |||
[ | <!--T:64--> | ||
Then edit ''/etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf'', under '''[Seat:*]''' replace the greeter-session setting with '''greeter-session=lightdm-slick-greeter''' | |||
====== Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for Cinnamon ====== <!--T:65--> | |||
sudo pacman -S manjaro-cinnamon-settings adapta-maia-theme kvantum-manjaro | |||
<!--T:66--> | |||
To configure LightDM to match the community edition replace the contents of /etc/lightdm/slick-greeter.conf with | |||
[Greeter] | |||
background=/usr/share/backgrounds/greeter_default.jpg | |||
background-color=#263138 | |||
draw-grid=false | |||
theme-name=Adapta-Nokto-Eta-Maia | |||
icon-theme-name=Papirus-Dark-Maia | |||
font-name='Cantarell 11' | |||
xft-antialias=true | |||
xft-hintstyle=hintfull | |||
enable-hidpi=auto | |||
<!--T:67--> | |||
Set the Manjaro logo on the panel by right-clicking on the menu and clicking configure. Select "Use a custom icon and label". Select the Manjaro icon. | |||
====== Create a new user for the new desktop environment ====== <!--T:68--> | |||
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> | |||
sudo passwd <username> | |||
<!--T:69--> | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
== | == Deepin == <!--T:70--> | ||
[[File: deepin.jpg|thumb|left|375px]] | |||
The '''[https://www.deepin.org/en/dde/ Deepin Desktop]''' is an elegant, easy to use desktop. It is lightly configurable. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running Deepin uses about 525MB of memory. | |||
====== Install a basic deepin environment ====== <!--T:71--> | |||
<!--T:72--> | |||
sudo pacman -S deepin | |||
====== Optional: Install the Deepin applications suite ====== <!--T:73--> | |||
sudo pacman -S deepin-extra | |||
====== Optional: Install and use LightDM, the recommended display manager for deepin====== <!--T:74--> | |||
sudo pacman -S | sudo pacman -S lightdm | ||
systemctl enable lightdm.service --force | |||
<!--T:75--> | |||
Then edit ''/etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf'', under '''[Seat:*]''' replace the greeter-session setting with '''greeter-session=lightdm-deepin-greeter''' | |||
sudo pacman -S | ====== Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for Deepin ====== <!--T:76--> | ||
sudo pacman -S deepin-manjaro | |||
====== Create a new user for the new desktop environment ====== <!--T:77--> | |||
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> | |||
sudo passwd <username> | |||
<!--T:78--> | |||
<br clear="all" /> | |||
== Enlightenment == <!--T:79--> | |||
{{note|There is not currently a Manjaro settings package for Enlightenment|}} | |||
[[File: E20-Green_Onix_760.png|thumb|left|375px]] | |||
<!--T:80--> | |||
'''[http://www.enlightenment.org/ Enlightenment]''', sometimes known simply as E, is a lightweight desktop environment known for its configurability and tools for creating beautiful user interfaces using its Enlightenment Foundation Libraries (EFL). E started in 1997 as a stacking window manager, emerging as a desktop environment since development release version 0.17. E does not come with a broad array of tools by default, which can be an advantage for experienced users who want to customize their installation, and a disadvantage for users with little or no experience of Linux. E uses a few unique terms, for example referring to panels as “shelves”. A 64-bit installation of E uses about 160M of memory. | |||
====== Install a basic E environment ====== <!--T:81--> | |||
sudo pacman -S enlightenment | |||
====== Optional: Install and use Entrance, the recommended display manager for E ====== <!--T:82--> | |||
Entrance is available from the AUR in the package '''entrance-git'''. Information on how to install packages from AUR can be found '''[https://wiki.manjaro.org/index.php/Arch_User_Repository here]'''. | |||
$ sudo pacman -S --asdeps meson | |||
$ pamac build entrance-git | |||
$ sudo systemctl enable entrance.service --force | |||
====== Optional: Install Manjaro themes for E ====== <!--T:83--> | |||
sudo pacman -S enlightenment-manjaro-themes | |||
====== Create a new user for the new desktop environment ====== <!--T:84--> | |||
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> | |||
sudo passwd <username> | |||
<!--T:85--> | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
== | == LXDE == <!--T:86--> | ||
<!--T:87--> | |||
{{Note|Installing LXDE will also result in installing ''Openbox'' as its default window manager. The LXDM display manager will also be downloaded, although it will be necessary to enable this yourself if you wish to replace your existing display manager.}} | |||
[[File: lxde17.1.11.jpg|thumb|left|375px]] | |||
<!--T:88--> | |||
'''[http://lxde.org/ LXDE]''' is a super-lightweight desktop environment that is very similar to XFCE, with the exception that it is not compatible with Compiz. As with XFCE, LXDE is also a somewhat basic desktop environment, lacking some modern features that would be expected, such as a search-bar to find applications and files. However, due to comparatively low resource requirements, it is also an excellent choice for less powerful computers. | |||
====== Install a basic LXDE environment ====== <!--T:89--> | |||
<!--T:90--> | |||
sudo pacman -S lxde network-manager-applet | |||
====== Optional: Install and use LightDM, the recommended display manager for lxde ====== <!--T:91--> | |||
sudo pacman -S lightdm lightdm-gtk-greeter lightdm-gtk-greeter-settings | |||
systemctl enable lightdm.service --force | |||
====== Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for lxde ====== <!--T:92--> | |||
sudo pacman -S manjaro-lxde-logout-banner manjaro-lxde-xfce4-notifyd manjaro-lxde-xfce4-volumed-pulse manjaro-settings-manager manjaro-settings-manager-notifier manjaro-lxde-settings arc-maia-icon-theme kvantum-manjaro | |||
<!--T:93--> | |||
To configure LightDM to match the community edition replace the contents of /etc/lightdm/lightdm-gtk-greeter.conf with | |||
[greeter] | |||
background = /usr/share/backgrounds/lxde-breath.png | |||
font-name = Cantarell 12 | |||
xft-antialias = true | |||
icon-theme-name = Arc-Maia | |||
screensaver-timeout = 60 | |||
theme-name = Adapta-Eta-Maia | |||
cursor-theme-name = xcursor-breeze | |||
show-clock = false | |||
default-user-image = #avatar-default | |||
xft-hintstyle = hintfull | |||
position = 50%,center 50%,center | |||
clock-format = | |||
panel-position = bottom | |||
====== Create a new user for the new desktop environment ====== <!--T:94--> | |||
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> | |||
sudo passwd <username> | |||
<!--T:95--> | |||
<br clear="all" /> | |||
== LXQt == <!--T:96--> | |||
<!--T:97--> | |||
[[File: Lxqt-de-18.png|thumb|left|375px]] | |||
<!--T:98--> | |||
The '''[https://lxqt-project.org/ LXQt Desktop Environment]''' LXQt is a lightweight Qt desktop environment. It was formed from the merger of the LXDE and Razor-qt projects. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running lxqt uses about 250MB of memory. | |||
====== Install a basic LXQt environment ====== <!--T:99--> | |||
sudo pacman -S lxqt xscreensaver | |||
====== Install and use LightDM, the recommended display manager for LXQt ====== <!--T:100--> | |||
sudo pacman -S lightdm lightdm-slick-greeter lightdm-settings light-locker | |||
systemctl enable lightdm.service --force | |||
edit /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf, under [Seat:*] replace the greeter-session setting with greeter-session=lightdm-slick-greeter | |||
====== Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for LXQt ====== <!--T:101--> | |||
sudo pacman -S manjaro-lxqt-extra-settings manjaro-openbox-adapta-maia papirus-maia-icon-theme | |||
====== Create a new user for the new desktop environment ====== <!--T:102--> | |||
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> | |||
sudo passwd <username> | |||
<!--T:103--> | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
== | == MATE == <!--T:104--> | ||
<!--T:105--> | |||
[[File: mate.jpg|thumb|left|375px]] | |||
<!--T:106--> | |||
'''[https://mate-desktop.org/ MATE]''' is a desktop environment and the continuation of GNOME 2. Featuring an intuitive and attractive desktop environment while preserving a traditional desktop experience, its aim is to maintain and continue the latest GNOME 2 code base, frameworks, and core applications. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running MATE uses about 378MB of memory. | |||
====== Install a basic MATE environment ====== <!--T:107--> | |||
<!--T:108--> | |||
sudo pacman -S mate network-manager-applet | |||
====== Optional: Install MATE applications and configuration tools ====== <!--T:109--> | |||
sudo pacman -S mate-extra dconf-editor | |||
''' | ====== Optional: Install and use LightDM, the recommended display manager for MATE ====== <!--T:110--> | ||
sudo pacman -S lightdm lightdm-slick-greeter lightdm-settings | |||
systemctl enable lightdm.service --force | |||
edit '''/etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf''', under [Seat:*] replace the greeter-session setting with '''greeter-session=lightdm-slick-greeter''' | |||
sudo pacman -S | ====== Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for MATE ====== <!--T:111--> | ||
sudo pacman -S manjaro-mate-settings arc-maia-icon-theme papirus-maia-icon-theme manjaro-settings-manager manjaro-settings-manager-notifier | |||
<!--T:112--> | |||
To configure LightDM to match the community edition replace the contents of /etc/lightdm/slick-greeter.conf with | |||
[Greeter] | |||
background=/usr/share/backgrounds/manjaro-mate/manjaro-mate.jpg | |||
theme-name=Adapta-Nokto-Maia | |||
icon-theme-name=Arc-Maia | |||
draw-grid=false | |||
====== Create a new user for the new desktop environment ====== <!--T:113--> | |||
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> | |||
sudo passwd <username> | |||
<!--T:114--> | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
= Window Managers = | = Window Managers = <!--T:115--> | ||
<!--T:116--> | |||
{{note|By nature, building your own desktop environment from a Window Manager will take substantially more time and effort than simply downloading a pre-defined desktop environment.}} | {{note|By nature, building your own desktop environment from a Window Manager will take substantially more time and effort than simply downloading a pre-defined desktop environment.}} | ||
<!--T:117--> | |||
{{warning|The images provided below are purely for illustrative purposes only. You will have you put in the necessary time and effort to configure them.}} | {{warning|The images provided below are purely for illustrative purposes only. You will have you put in the necessary time and effort to configure them.}} | ||
Although | <!--T:118--> | ||
Although desktop environments commonly provide a good range of customisation options to suit personal taste and preference, they may still be seen as somewhat restrictive or controlled in the sense that they merely allow for the personalisation of their pre-defined components. However, certain Window Managers (WM) empower users to take a 'do it yourself' approach in order to create their own desktop environments. In essence, they may be used as a foundation on which to build upon, as literally every component and every aspect of the desktop is under the direct control and choice of the user. An environment may be as elaborate or as minimalistic as desired, and it is even possible to mix and match various components from other desktop environments. | |||
<!--T:119--> | |||
Therefore extremely powerful and versatile, these window managers also carry the additional benefit of being faster and more resource efficient than pre-defined desktop environments. Interestingly, the super-lightweight LXDE environment is itself built on the Openbox window manager. There are two types of Window Manager: '''Stacking''' and '''Tiling'''. These names denote how application windows will behave on your desktop. | Therefore extremely powerful and versatile, these window managers also carry the additional benefit of being faster and more resource efficient than pre-defined desktop environments. Interestingly, the super-lightweight LXDE environment is itself built on the Openbox window manager. There are two types of Window Manager: '''Stacking''' and '''Tiling'''. These names denote how application windows will behave on your desktop. | ||
== Stacking Window Managers == <!--T:120--> | |||
<!--T:121--> | |||
'''Stacking window managers''' are by far the most popular, and essentially allow application windows to be moved freely around the screen, which may overlap - or 'stack' - upon one another, hence the name. All popular desktop environments such as Xfce, KDE Plasma and GNOME use stacking window Managers. | |||
=== Openbox === <!--T:122--> | |||
<!--T:123--> | |||
[[File: manjarobox.png|thumb|left|375px]] | |||
<!--T:124--> | |||
'''[http://openbox.org/ Openbox]''' is by far the most popular Window Manager available. Due to its popularity there is excellent documentation available, as well as a good choice of additional themes that may be downloaded. '''To install Openbox, enter the command:''' | |||
<!--T:125--> | |||
sudo pacman -S openbox | |||
<!--T:126--> | |||
To install a logout script, configuration application, menu-editor, and extra themes for Openbox, enter the following command: | |||
sudo pacman -S openbox | <!--T:127--> | ||
sudo pacman -S oblogout obconf lxappearance-obconf-gtk3 obmenu openbox-themes-extra | |||
====== Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration, theming, and tools for Openbox ====== <!--T:128--> | |||
sudo pacman -S oblogout | <!--T:129--> | ||
sudo pacman -S oblogout-manjaro manjaro-openbox-config manjaro-openbox-scripts manjaro-openbox-fonts matcha-gtk-theme | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
=== FluxBox === | === FluxBox === <!--T:130--> | ||
<!--T:131--> | |||
[[File: fluxbox2.png|thumb|left|375px]] | [[File: fluxbox2.png|thumb|left|375px]] | ||
<!--T:132--> | |||
'''[http://fluxbox.org/ FluxBox]''' is another popular Window Manager. It is particularly notable for providing some features not seen in Openbox, such as ''tabbing'', which allows for windows to be grouped together. '''To install FluxBox, enter the command''': | '''[http://fluxbox.org/ FluxBox]''' is another popular Window Manager. It is particularly notable for providing some features not seen in Openbox, such as ''tabbing'', which allows for windows to be grouped together. '''To install FluxBox, enter the command''': | ||
sudo pacman -S fluxbox | <!--T:133--> | ||
sudo pacman -S fluxbox | |||
====== Optional: Install the newsfetcher and workspace pager for Fluxbox ====== <!--T:134--> | |||
<!--T:135--> | |||
sudo pacman -S fbnews fluxter | |||
====== Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration, theming, and tools for Fluxbox ====== <!--T:136--> | |||
sudo pacman -S | <!--T:137--> | ||
sudo pacman -S fbmenu-manjaro oblogout-manjaro artwork-fluxbox fluxboxtheme-manjaro | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
=== IceWM === <!--T:138--> | |||
<!--T:139--> | |||
[[File: icewm2.jpg|thumb|left|375px]] | [[File: icewm2.jpg|thumb|left|375px]] | ||
'''[ | <!--T:140--> | ||
'''[https://www.ice-wm.org/ IceWM]''' is a Window Manager notable for perhaps being closer to a full desktop environment than Openbox or FluxBox. This includes providing a panel complete with menu, in addition to a workspace switcher. '''To install IceWM, enter the command''': | |||
sudo pacman -S icewm | <!--T:141--> | ||
sudo pacman -S icewm | |||
<!--T:142--> | |||
To install a suite of tools and themes specifically for IceWM, enter the command: | To install a suite of tools and themes specifically for IceWM, enter the command: | ||
sudo pacman -S icewm-utils icewm-themes | <!--T:143--> | ||
sudo pacman -S icewm-utils icewm-themes | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
== Tiling Window Managers == <!--T:144--> | |||
<!--T:145--> | |||
'''Tiling window managers''' - as the name would suggest - tile application windows; each will have their own place on the screen, just like conventional tiles do not overlap. However, unlike conventional tiling, these window managers are usually very flexible, and allow for a multitude of different tiling patterns to suit personal taste and preference. Where stacking window managers focus on using the mouse for navigation, tiling window managers focus on the utilisation of the keyboard instead. As such, they can be much faster to use. | '''Tiling window managers''' - as the name would suggest - tile application windows; each will have their own place on the screen, just like conventional tiles do not overlap. However, unlike conventional tiling, these window managers are usually very flexible, and allow for a multitude of different tiling patterns to suit personal taste and preference. Where stacking window managers focus on using the mouse for navigation, tiling window managers focus on the utilisation of the keyboard instead. As such, they can be much faster to use. | ||
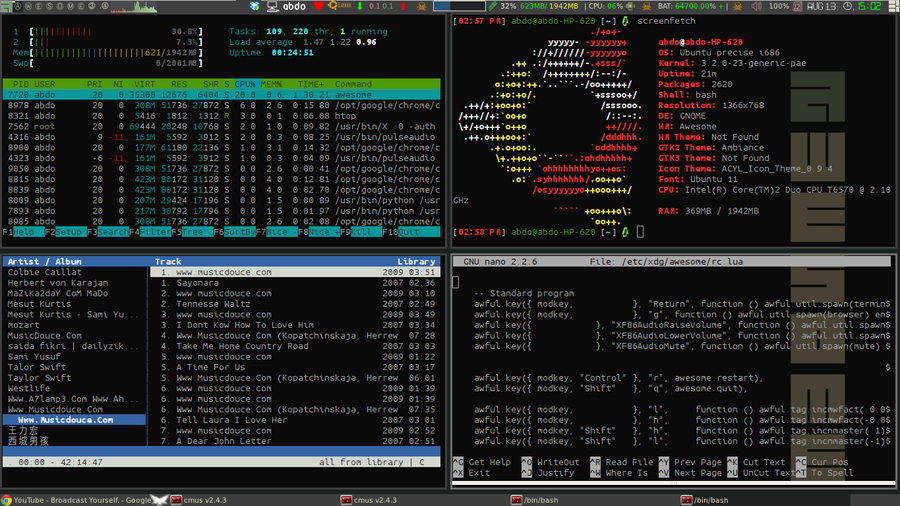
=== Awesome === | === Awesome === <!--T:146--> | ||
<!--T:147--> | |||
[[File: awesome.png|thumb|left|375px]] | [[File: awesome.png|thumb|left|375px]] | ||
'''[http://awesome.naquadah.org/ Awesome]''' is a popular tiling Window Manager, notable for using the '''Lua''' | <!--T:148--> | ||
'''[http://awesome.naquadah.org/ Awesome]''' is a popular tiling Window Manager, notable for using the '''Lua''' language for configuration. '''To install Awesome, enter the command''': | |||
sudo pacman -S awesome | <!--T:149--> | ||
sudo pacman -S awesome | |||
<!--T:150--> | |||
To install some extra widgets for Awesome, enter the command: | To install some extra widgets for Awesome, enter the command: | ||
sudo pacman -S vicious | <!--T:151--> | ||
sudo pacman -S vicious | |||
<!--T:152--> | |||
Alternatively you can install the [[Awesome Community Edition]]. | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
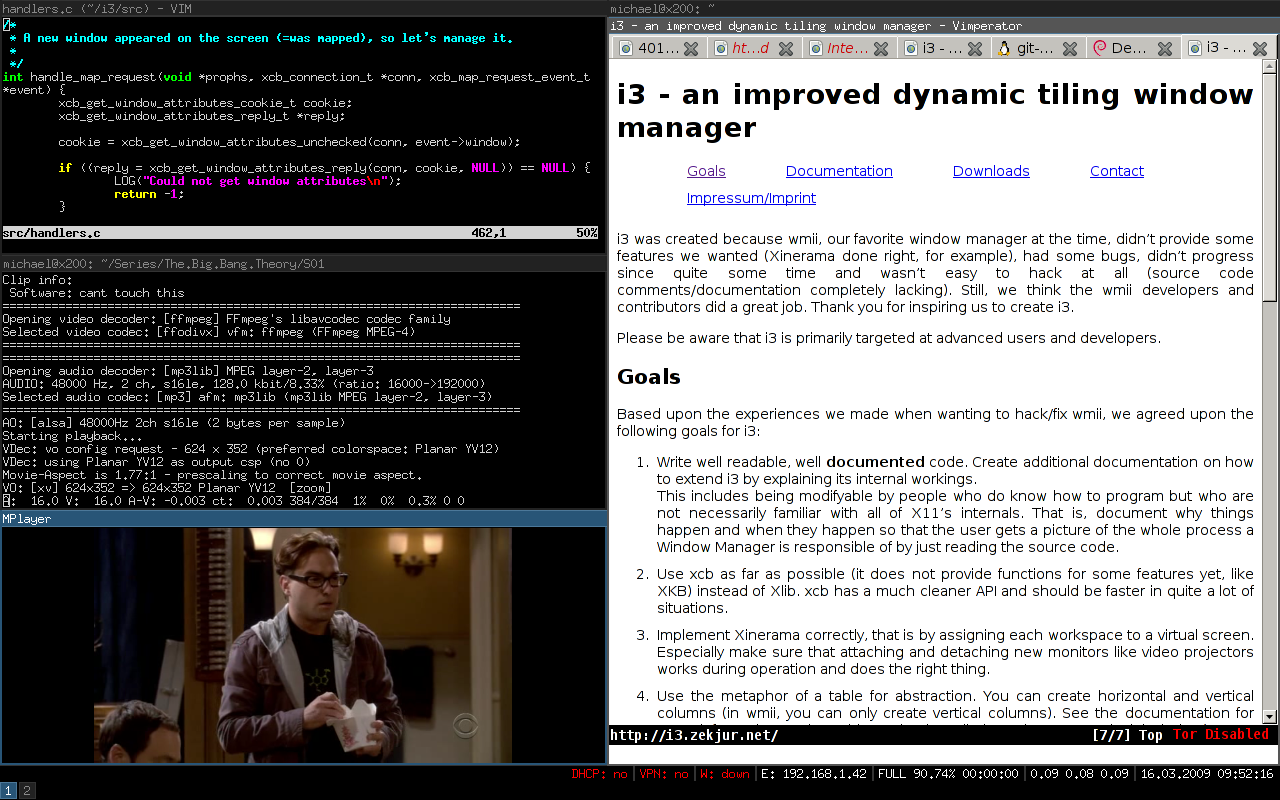
=== i3 === <!--T:153--> | |||
<!--T:154--> | |||
[[File: i3wm.png|thumb|left|375px]] | [[File: i3wm.png|thumb|left|375px]] | ||
<!--T:155--> | |||
'''[http://i3wm.org/ i3]''' is arguably the most popular tiling window manager available, and notable for using a single, completely self-contained configuration file. '''To install i3, enter the command''': | '''[http://i3wm.org/ i3]''' is arguably the most popular tiling window manager available, and notable for using a single, completely self-contained configuration file. '''To install i3, enter the command''': | ||
sudo pacman -S i3-wm | <!--T:156--> | ||
sudo pacman -S i3-wm | |||
<!--T:157--> | |||
To install a status bar and screen-locker for i3, enter the command: | To install a status bar and screen-locker for i3, enter the command: | ||
sudo pacman -S i3lock i3status | <!--T:158--> | ||
sudo pacman -S i3lock i3status | |||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
</translate> | |||
[[Category:Contents Page{{#translation:}}]] | |||
[[Category:Editions{{#translation:}}]] | |||
[[Category: | |||
Latest revision as of 05:16, 27 May 2024
Overview
There are several desktop environments and window managers available for Manjaro, each with their own unique style, interface, and features. Furthermore, it is possible to install multiple environments if desired, which can be selected at the login screen at any time. Users are not restricted to whatever comes pre-installed with a particular flavour of Manjaro.
Desktop Environments
It is worth noting that a desktop environment (DE) is not a single entity; it is actually a collection of different components that work together. This commonly includes a:
- window manager to display, move and resize application windows
- file manager to visually browse, copy and access files, etc.
- background provider to display wallpapers, etc.
- panel to provide a menu and to display information such as the time
- settings/configuration manager to change the look of the environment
And so on. Most desktop environments will also come with their own preferred applications, in addition to various widgets, addons, and extensions to provide extra features. As such, upon entering the commands provided below in your terminal to download and install a desktop environment, you may be prompted to choose from a selection of components provided for it. To install a full desktop environment - complete with its own preferred file manager, applications, and so on
Where additional (and optional) extras for a desktop environment are available, the terminal commands to obtain these have also been provided.
Some important information about installing the Manjaro settings packages:
- The Manjaro settings packages contain the theming and settings to make the desktop the same as in the Manjaro ISOs
- They have the naming convention manjaro-<desktop>-settings i.e. manjaro-xfce-settings
- They share files so you can only have one at a time installed.
- If you are coming from gnome you must remove the meta package manjaro-gnome-assets before you can install the settings package for another desktop
The Risks of Using Multiple DEs
Installing multiple DEs is not without risks. Here are some things that can pop-up when running more than one DE:
- The settings packages overlap so you can only have one DE pre-configured with the Manjaro theming. The others will need to have the theming applied manually.
- You can end up with more than one instance of similar applications. For example, it is common to end up with 2 Bluetooth managers. It takes some tweaking to get a single manager working in multiple DEs.
- Sometimes two different DEs will share the same configuration files causing strange things to happen, especially with theming.
These risks are greatly reduced by using a different user account for each DE.
In summary, running multiple DEs is possible and a great way to enjoy Manjaro but it requires a willingness to troubleshoot and work through minor problems. If you are the type of person who wants everything to "just work" out of the box, running multiple DEs might not be for you.
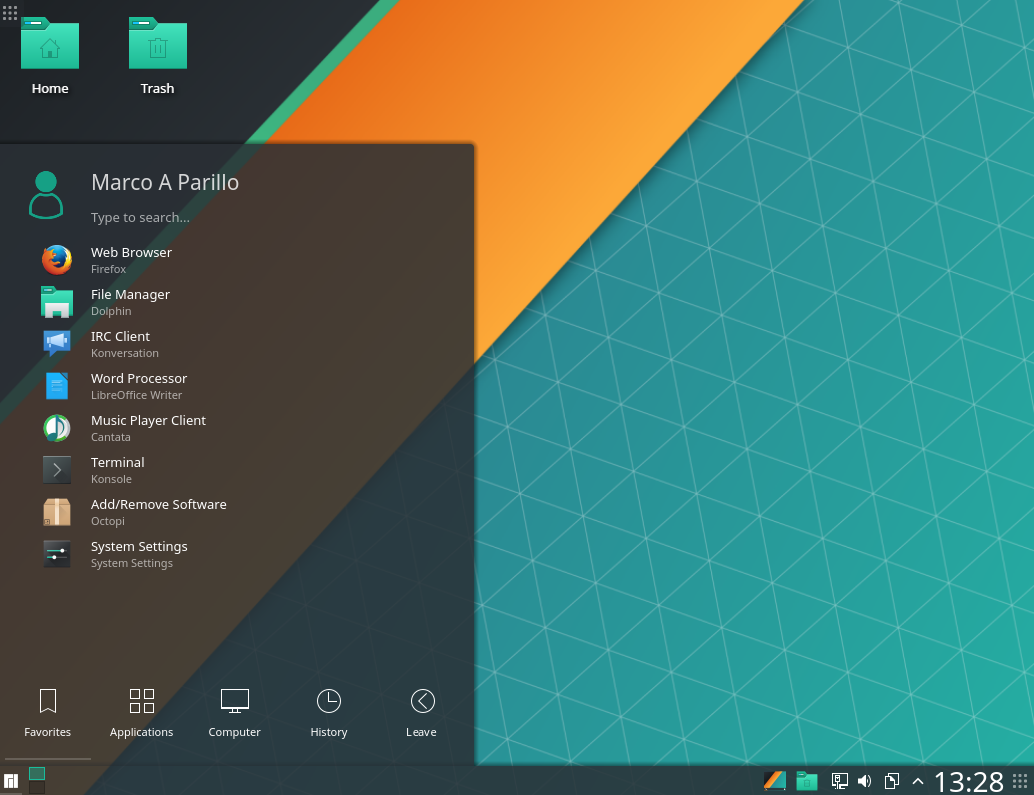
Xfce
Xfce or XFCE, pronounced as four individual letters, is a lightweight and versatile desktop environment that utilises a classic drop-down/pop-up menu to access applications. It is also compatible with Compiz. A little time and effort will also be required to properly customise the desktop to suit personal taste. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running Xfce uses about 390MB of memory. As of version 18, Manjaro has moved to the gtk3 version of Xfce.
Install a basic Xfce environment
sudo pacman -S xfce4 xfce4-goodies xfce4-terminal network-manager-applet xfce4-notifyd xfce4-whiskermenu-plugin tumbler engrampa
Optional: Install and use LightDM, the recommended display manager for Xfce
sudo pacman -S lightdm lightdm-gtk-greeter lightdm-gtk-greeter-settings sudo systemctl enable lightdm.service --force
edit /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf, under [Seat:*] replace the greeter-session setting with greeter-session=lightdm-gtk-greeter
Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for Xfce
sudo pacman -S manjaro-xfce-settings manjaro-settings-manager
To configure LightDM to match the official iso replace the contents of /etc/lightdm/lightdm-gtk-greeter.conf with
[greeter] background = /usr/share/backgrounds/illyria-default-lockscreen.jpg font-name = Cantarell Bold 12 xft-antialias = true icon-theme-name = Papirus screensaver-timeout = 60 theme-name = Matcha-azul cursor-theme-name = xcursor-breeze show-clock = false default-user-image = #avatar-default xft-hintstyle = hintfull position = 50%,center 50%,center clock-format = panel-position = bottom indicators = ~host;~spacer;~clock;~spacer;~language;~session;~a11y;~power
Create a new user for the new desktop environment
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> sudo passwd <username>
KDE Plasma 6
The KDE community offers Plasma, a feature-rich and versatile desktop environment that provides several different styles of menu to access applications. An excellent built-in interface to easily access and install new themes, widgets, etc, from the internet is also worth mentioning. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running KDE uses about 455MB of memory.
Install a basic KDE Plasma environment
sudo pacman -S plasma kio-extras
Optional: Install KDE applications
To install a full set of K* applications use kde-applications-meta. This will be ~300 packages(including dependencies)
sudo pacman -S kde-applications-meta
Optional: Install and use SDDM, the recommended display manager for KDE
SDDM is installed as a dependency of plasma. To enable it
systemctl enable sddm.service --force systemctl reboot
Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for plasma
sudo pacman -S manjaro-kde-settings sddm-breath-theme manjaro-settings-manager
Open plasma settings, go to Startup & Shutdown->Login Screen and select "Breath"
Alternatively, the newer themes may be installed with:
sudo pacman -S plasmat-themes-breath
Create a new user for the new desktop environment
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,wheel <username> sudo passwd <username>
GNOME 3
GNOME 3 is an intuitive desktop environment that utilises a tablet or smartphone style interface to access applications. It is not compatible with compiz. Although GNOME is very easy to learn and use, it has limited customisation options and it can be difficult to configure. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running GNOME uses about 447MB of memory.
Install a basic GNOME environment
sudo pacman -S gnome
Optional: To install extra themes, games, and features
sudo pacman -S gnome-extra
Optional: Install and use GDM, the recommended display manager for GNOME
GDM is installed as a dependency of GNOME. To enable it:
systemctl enable gdm.service --force
Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for GNOME
sudo pacman -S manjaro-gnome-settings manjaro-settings-manager
Create a new user for the new desktop environment
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> sudo passwd <username>
Budgie
The Budgie Desktop is a modern desktop designed to keep out the way of the user. It features heavy integration with the GNOME stack in order for an enhanced experience. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running Budgie uses about 632MB of memory.
Install a basic Budgie environment
sudo pacman -S budgie-desktop network-manager-applet gnome-control-center gnome-screensaver
Optional: Install additional commonly used components
sudo pacman -S gnome-terminal nautilus budgie-extras dconf-editor
Optional: Install and use LightDM, the recommended display manager for budgie
sudo pacman -S lightdm lightdm-slick-greeter lightdm-settings systemctl enable lightdm.service --force
edit /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf, under [Seat:*] replace the greeter-session setting with greeter-session=lightdm-slick-greeter
Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for Budgie
sudo pacman -S manjaro-budgie-settings manjaro-settings-manager papirus-maia-icon-theme
To configure LightDM to match the official iso replace the contents of /etc/lightdm/slick-greeter.conf with
[Greeter] background=/usr/share/backgrounds/manjaro-budgie/manjaro-budgie.jpg theme-name=Matcha-sea icon-theme-name=Papirus-Maia draw-grid=false
Create a new user for the new desktop environment
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> sudo passwd <username>
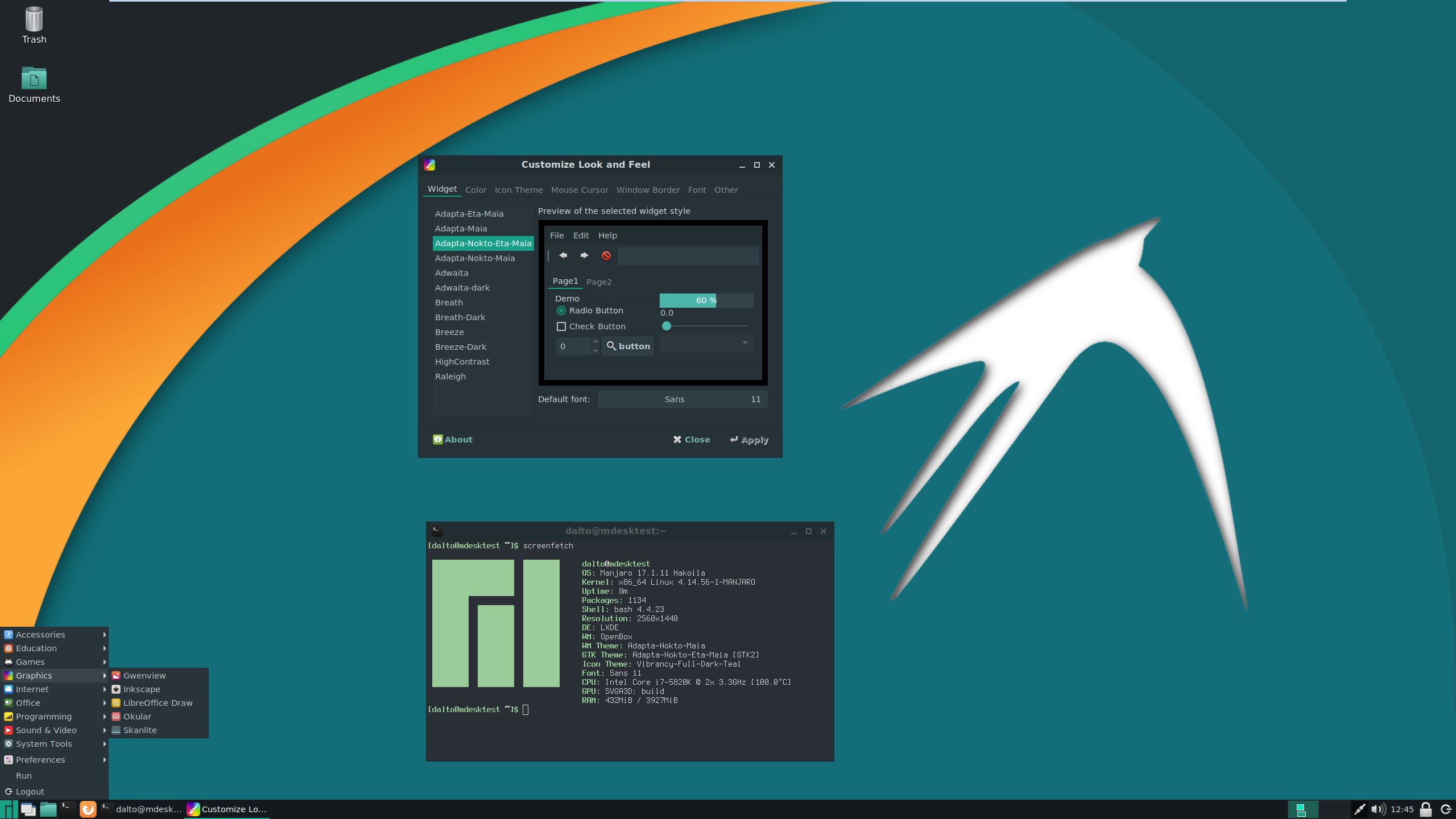
Cinnamon
Cinnamon is a desktop environment based on GNOME 3 that utilises a large panel-style menu to access applications. It is not compatible with compiz. Despite being based on GNOME, it has more customisation options and therefore is easier to configure. Windows Vista or 7 users may find Cinnamon's interface comfortably familiar. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running Cinnamon uses about 665MB of memory.
Install a basic Cinnamon environment
sudo pacman -S cinnamon
Optional: Install additional commonly used components
sudo pacman -S cinnamon-wallpapers cinnamon-sounds gnome-terminal parcellite
Optional: Install and use LightDM, the recommended display manager for cinnamon
sudo pacman -S lightdm lightdm-slick-greeter lightdm-settings systemctl enable lightdm.service --force
Then edit /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf, under [Seat:*] replace the greeter-session setting with greeter-session=lightdm-slick-greeter
Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for Cinnamon
sudo pacman -S manjaro-cinnamon-settings adapta-maia-theme kvantum-manjaro
To configure LightDM to match the community edition replace the contents of /etc/lightdm/slick-greeter.conf with
[Greeter] background=/usr/share/backgrounds/greeter_default.jpg background-color=#263138 draw-grid=false theme-name=Adapta-Nokto-Eta-Maia icon-theme-name=Papirus-Dark-Maia font-name='Cantarell 11' xft-antialias=true xft-hintstyle=hintfull enable-hidpi=auto
Set the Manjaro logo on the panel by right-clicking on the menu and clicking configure. Select "Use a custom icon and label". Select the Manjaro icon.
Create a new user for the new desktop environment
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> sudo passwd <username>
Deepin
The Deepin Desktop is an elegant, easy to use desktop. It is lightly configurable. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running Deepin uses about 525MB of memory.
Install a basic deepin environment
sudo pacman -S deepin
Optional: Install the Deepin applications suite
sudo pacman -S deepin-extra
Optional: Install and use LightDM, the recommended display manager for deepin
sudo pacman -S lightdm systemctl enable lightdm.service --force
Then edit /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf, under [Seat:*] replace the greeter-session setting with greeter-session=lightdm-deepin-greeter
Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for Deepin
sudo pacman -S deepin-manjaro
Create a new user for the new desktop environment
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> sudo passwd <username>
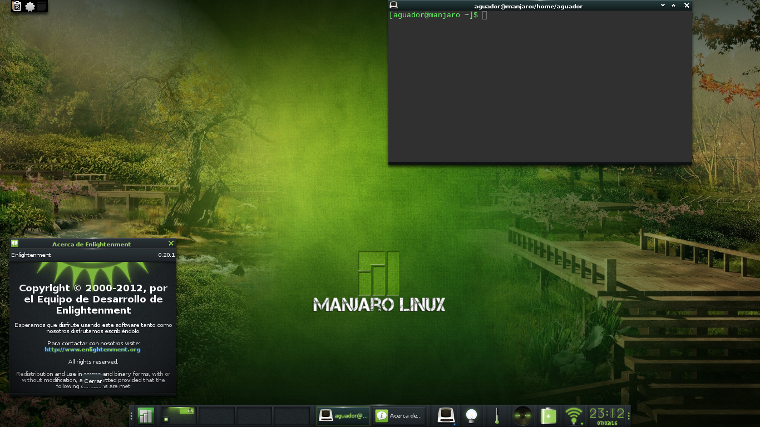
Enlightenment
Enlightenment, sometimes known simply as E, is a lightweight desktop environment known for its configurability and tools for creating beautiful user interfaces using its Enlightenment Foundation Libraries (EFL). E started in 1997 as a stacking window manager, emerging as a desktop environment since development release version 0.17. E does not come with a broad array of tools by default, which can be an advantage for experienced users who want to customize their installation, and a disadvantage for users with little or no experience of Linux. E uses a few unique terms, for example referring to panels as “shelves”. A 64-bit installation of E uses about 160M of memory.
Install a basic E environment
sudo pacman -S enlightenment
Optional: Install and use Entrance, the recommended display manager for E
Entrance is available from the AUR in the package entrance-git. Information on how to install packages from AUR can be found here.
$ sudo pacman -S --asdeps meson $ pamac build entrance-git $ sudo systemctl enable entrance.service --force
Optional: Install Manjaro themes for E
sudo pacman -S enlightenment-manjaro-themes
Create a new user for the new desktop environment
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> sudo passwd <username>
LXDE
LXDE is a super-lightweight desktop environment that is very similar to XFCE, with the exception that it is not compatible with Compiz. As with XFCE, LXDE is also a somewhat basic desktop environment, lacking some modern features that would be expected, such as a search-bar to find applications and files. However, due to comparatively low resource requirements, it is also an excellent choice for less powerful computers.
Install a basic LXDE environment
sudo pacman -S lxde network-manager-applet
Optional: Install and use LightDM, the recommended display manager for lxde
sudo pacman -S lightdm lightdm-gtk-greeter lightdm-gtk-greeter-settings systemctl enable lightdm.service --force
Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for lxde
sudo pacman -S manjaro-lxde-logout-banner manjaro-lxde-xfce4-notifyd manjaro-lxde-xfce4-volumed-pulse manjaro-settings-manager manjaro-settings-manager-notifier manjaro-lxde-settings arc-maia-icon-theme kvantum-manjaro
To configure LightDM to match the community edition replace the contents of /etc/lightdm/lightdm-gtk-greeter.conf with
[greeter] background = /usr/share/backgrounds/lxde-breath.png font-name = Cantarell 12 xft-antialias = true icon-theme-name = Arc-Maia screensaver-timeout = 60 theme-name = Adapta-Eta-Maia cursor-theme-name = xcursor-breeze show-clock = false default-user-image = #avatar-default xft-hintstyle = hintfull position = 50%,center 50%,center clock-format = panel-position = bottom
Create a new user for the new desktop environment
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> sudo passwd <username>
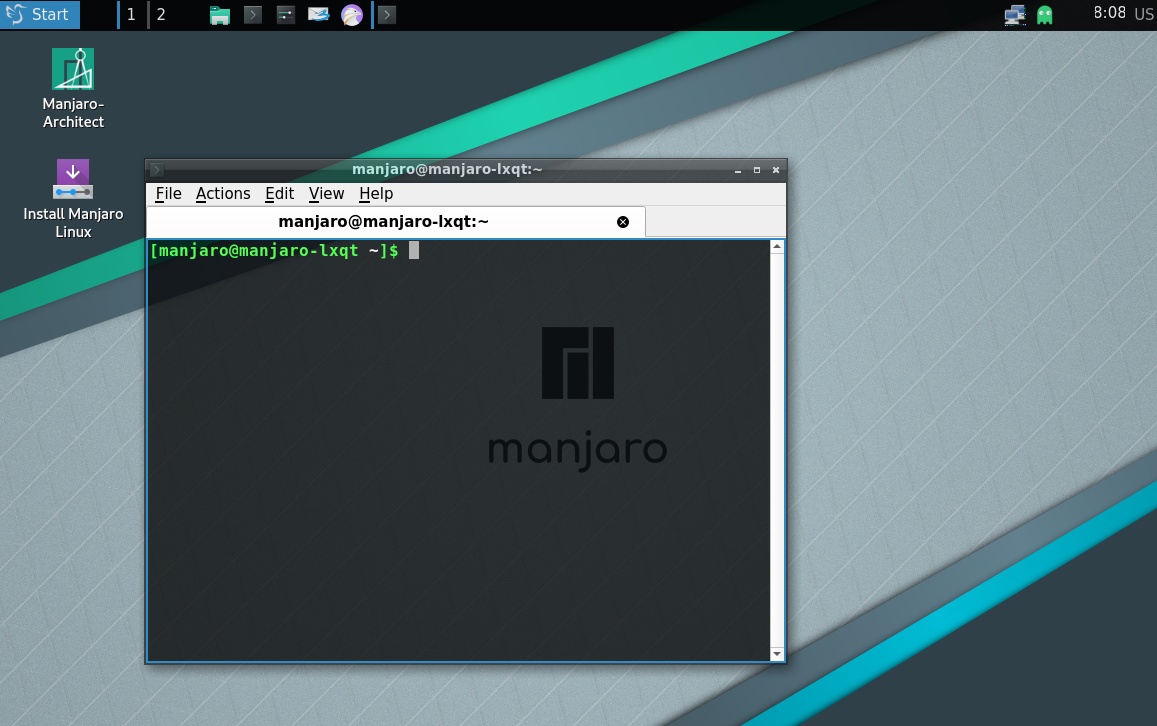
LXQt
The LXQt Desktop Environment LXQt is a lightweight Qt desktop environment. It was formed from the merger of the LXDE and Razor-qt projects. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running lxqt uses about 250MB of memory.
Install a basic LXQt environment
sudo pacman -S lxqt xscreensaver
Install and use LightDM, the recommended display manager for LXQt
sudo pacman -S lightdm lightdm-slick-greeter lightdm-settings light-locker systemctl enable lightdm.service --force
edit /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf, under [Seat:*] replace the greeter-session setting with greeter-session=lightdm-slick-greeter
Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for LXQt
sudo pacman -S manjaro-lxqt-extra-settings manjaro-openbox-adapta-maia papirus-maia-icon-theme
Create a new user for the new desktop environment
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> sudo passwd <username>
MATE
MATE is a desktop environment and the continuation of GNOME 2. Featuring an intuitive and attractive desktop environment while preserving a traditional desktop experience, its aim is to maintain and continue the latest GNOME 2 code base, frameworks, and core applications. A 64 bit installation of Manjaro running MATE uses about 378MB of memory.
Install a basic MATE environment
sudo pacman -S mate network-manager-applet
Optional: Install MATE applications and configuration tools
sudo pacman -S mate-extra dconf-editor
Optional: Install and use LightDM, the recommended display manager for MATE
sudo pacman -S lightdm lightdm-slick-greeter lightdm-settings systemctl enable lightdm.service --force
edit /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf, under [Seat:*] replace the greeter-session setting with greeter-session=lightdm-slick-greeter
Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration and theming for MATE
sudo pacman -S manjaro-mate-settings arc-maia-icon-theme papirus-maia-icon-theme manjaro-settings-manager manjaro-settings-manager-notifier
To configure LightDM to match the community edition replace the contents of /etc/lightdm/slick-greeter.conf with
[Greeter] background=/usr/share/backgrounds/manjaro-mate/manjaro-mate.jpg theme-name=Adapta-Nokto-Maia icon-theme-name=Arc-Maia draw-grid=false
Create a new user for the new desktop environment
sudo useradd -mG lp,network,power,sys,wheel <username> sudo passwd <username>
Window Managers
Although desktop environments commonly provide a good range of customisation options to suit personal taste and preference, they may still be seen as somewhat restrictive or controlled in the sense that they merely allow for the personalisation of their pre-defined components. However, certain Window Managers (WM) empower users to take a 'do it yourself' approach in order to create their own desktop environments. In essence, they may be used as a foundation on which to build upon, as literally every component and every aspect of the desktop is under the direct control and choice of the user. An environment may be as elaborate or as minimalistic as desired, and it is even possible to mix and match various components from other desktop environments.
Therefore extremely powerful and versatile, these window managers also carry the additional benefit of being faster and more resource efficient than pre-defined desktop environments. Interestingly, the super-lightweight LXDE environment is itself built on the Openbox window manager. There are two types of Window Manager: Stacking and Tiling. These names denote how application windows will behave on your desktop.
Stacking Window Managers
Stacking window managers are by far the most popular, and essentially allow application windows to be moved freely around the screen, which may overlap - or 'stack' - upon one another, hence the name. All popular desktop environments such as Xfce, KDE Plasma and GNOME use stacking window Managers.
Openbox
Openbox is by far the most popular Window Manager available. Due to its popularity there is excellent documentation available, as well as a good choice of additional themes that may be downloaded. To install Openbox, enter the command:
sudo pacman -S openbox
To install a logout script, configuration application, menu-editor, and extra themes for Openbox, enter the following command:
sudo pacman -S oblogout obconf lxappearance-obconf-gtk3 obmenu openbox-themes-extra
Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration, theming, and tools for Openbox
sudo pacman -S oblogout-manjaro manjaro-openbox-config manjaro-openbox-scripts manjaro-openbox-fonts matcha-gtk-theme
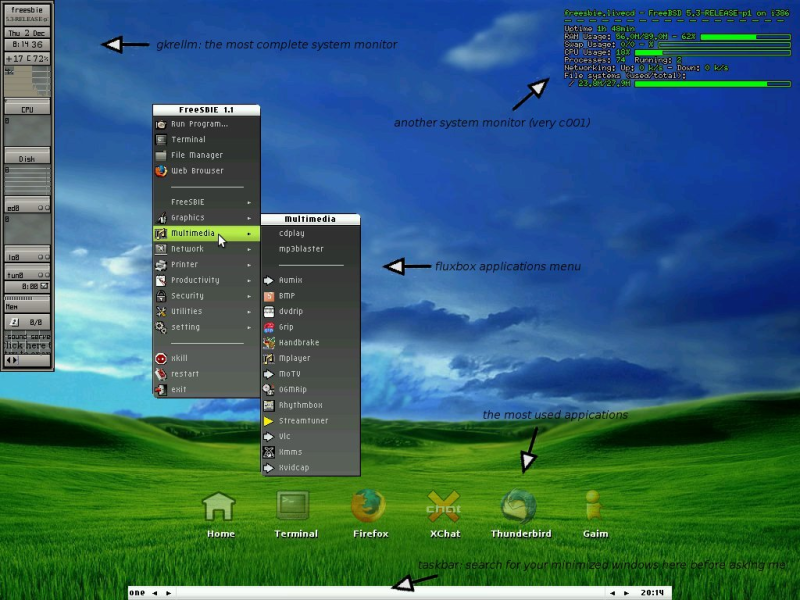
FluxBox
FluxBox is another popular Window Manager. It is particularly notable for providing some features not seen in Openbox, such as tabbing, which allows for windows to be grouped together. To install FluxBox, enter the command:
sudo pacman -S fluxbox
Optional: Install the newsfetcher and workspace pager for Fluxbox
sudo pacman -S fbnews fluxter
Optional: Install the Manjaro configuration, theming, and tools for Fluxbox
sudo pacman -S fbmenu-manjaro oblogout-manjaro artwork-fluxbox fluxboxtheme-manjaro
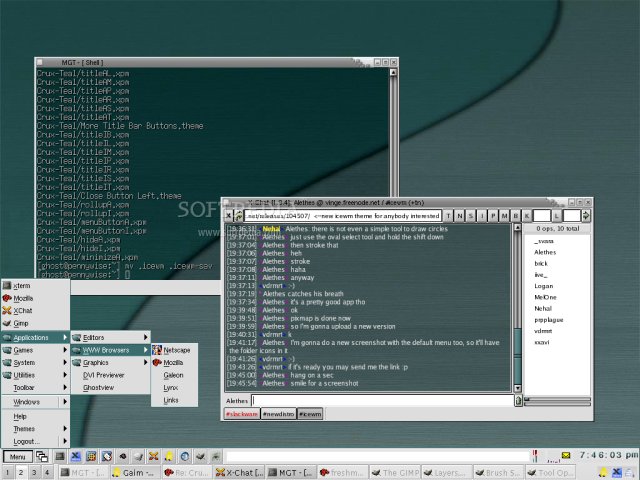
IceWM
IceWM is a Window Manager notable for perhaps being closer to a full desktop environment than Openbox or FluxBox. This includes providing a panel complete with menu, in addition to a workspace switcher. To install IceWM, enter the command:
sudo pacman -S icewm
To install a suite of tools and themes specifically for IceWM, enter the command:
sudo pacman -S icewm-utils icewm-themes
Tiling Window Managers
Tiling window managers - as the name would suggest - tile application windows; each will have their own place on the screen, just like conventional tiles do not overlap. However, unlike conventional tiling, these window managers are usually very flexible, and allow for a multitude of different tiling patterns to suit personal taste and preference. Where stacking window managers focus on using the mouse for navigation, tiling window managers focus on the utilisation of the keyboard instead. As such, they can be much faster to use.
Awesome
Awesome is a popular tiling Window Manager, notable for using the Lua language for configuration. To install Awesome, enter the command:
sudo pacman -S awesome
To install some extra widgets for Awesome, enter the command:
sudo pacman -S vicious
Alternatively you can install the Awesome Community Edition.
i3
i3 is arguably the most popular tiling window manager available, and notable for using a single, completely self-contained configuration file. To install i3, enter the command:
sudo pacman -S i3-wm
To install a status bar and screen-locker for i3, enter the command:
sudo pacman -S i3lock i3status