Difference between revisions of "Flatpak"
Views
Actions
Namespaces
Variants
Tools
imported>Dalto (Initial revision) |
imported>Dalto (Added instructions for removing Flatpak) |
||
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
You can remove Flatpaks with the command {{ic|flatpak uninstall}}. For example: | You can remove Flatpaks with the command {{ic|flatpak uninstall}}. For example: | ||
flatpak uninstall org.videolan.VLC | flatpak uninstall org.videolan.VLC | ||
=Removing Flatpak Support= | |||
If you no longer wish to have support for the Flatpack in your system you can remove it from the system by simply removing the package {{ic|flatpak}} with your favorite package manager or with the command | |||
pamac remove flatpak | |||
To also remove any installed Flatpaks you need to remove the directories containing them. These are {{ic|/var/lib/flatpak}} and {{ic|~/.local/share/flatpak}}. For example, you could use the command | |||
sudo rm -r /var/lib/flatpak | |||
rm -r ~/.local/share/flatpak | |||
[[Category:Contents Page]] | [[Category:Contents Page]] | ||
Revision as of 14:49, 7 July 2019
Overview
Flatpak is a distro independent method for packaging and distributing Linux software.
Using software distributed by Flatpak has a couple of distinct advantages:
- Software that is not compatible with current system libraries will still work when packaged as a Flatpak
- Delta upgrades make upgrades more network efficient in the long-term
There are some other considerations to be aware of:
- Flatpaks are not updated as part of your system updates, they must be updated separately
- Only themes that have been ported to Flatpak will work with Flatpaks
- A large set of shared runtimes will need to be installed to use Flatpaks
Installing Flatpak
Flatpak is available in the Manjaro repos as flatpak and can be installed with your favorite package manager or using the command
pamac install flatpak
Using Flatpak
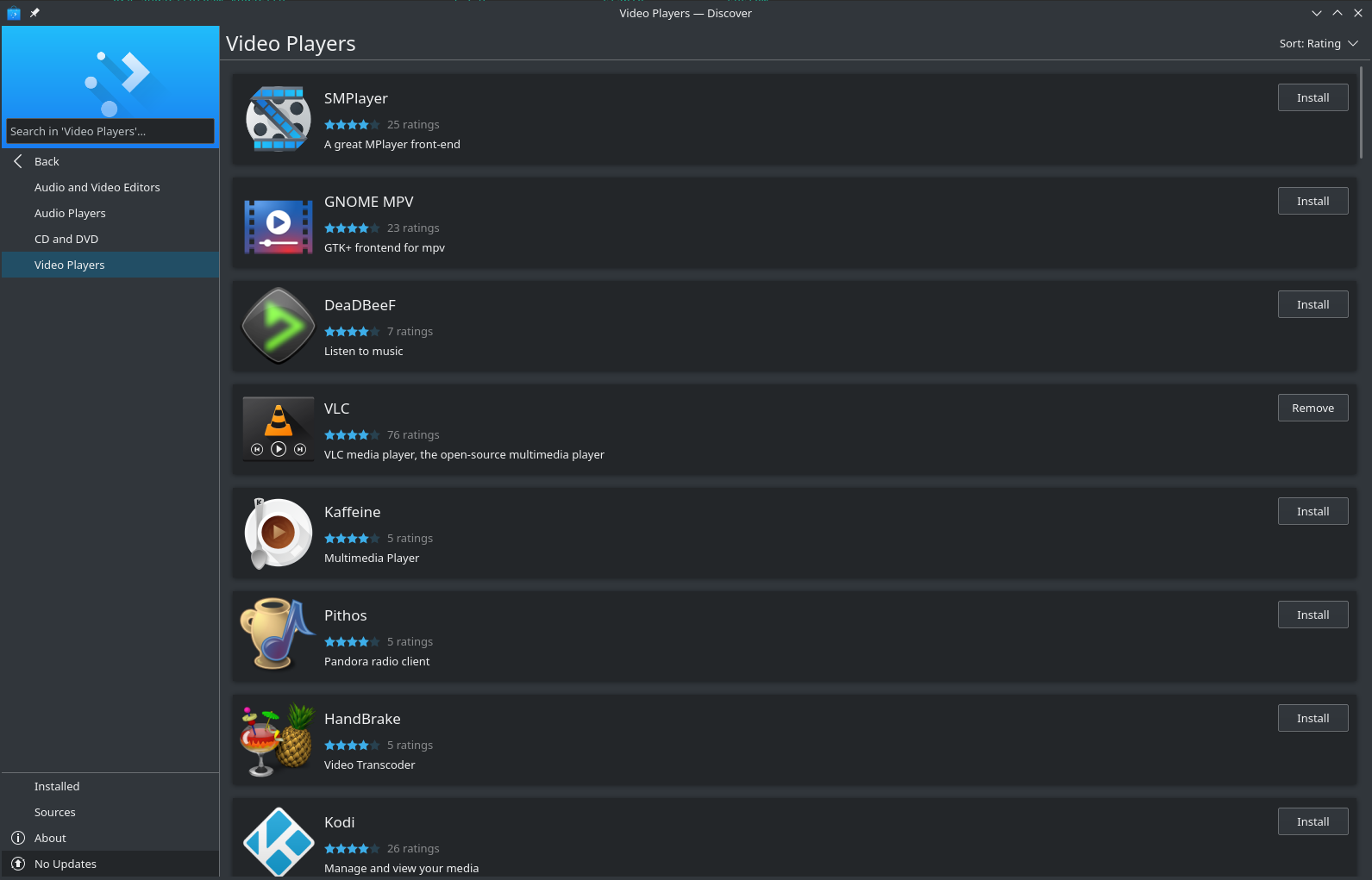
Managing Flatpaks via Discover
One way to manage your Flatpaks is with the application Discover from the KDE project. You can install the package discover with your favorite package manager or the command:
pamac install discover
Once installed you can run Discover and you will be able to browse, install and update Flatpaks with a familiar store interface.
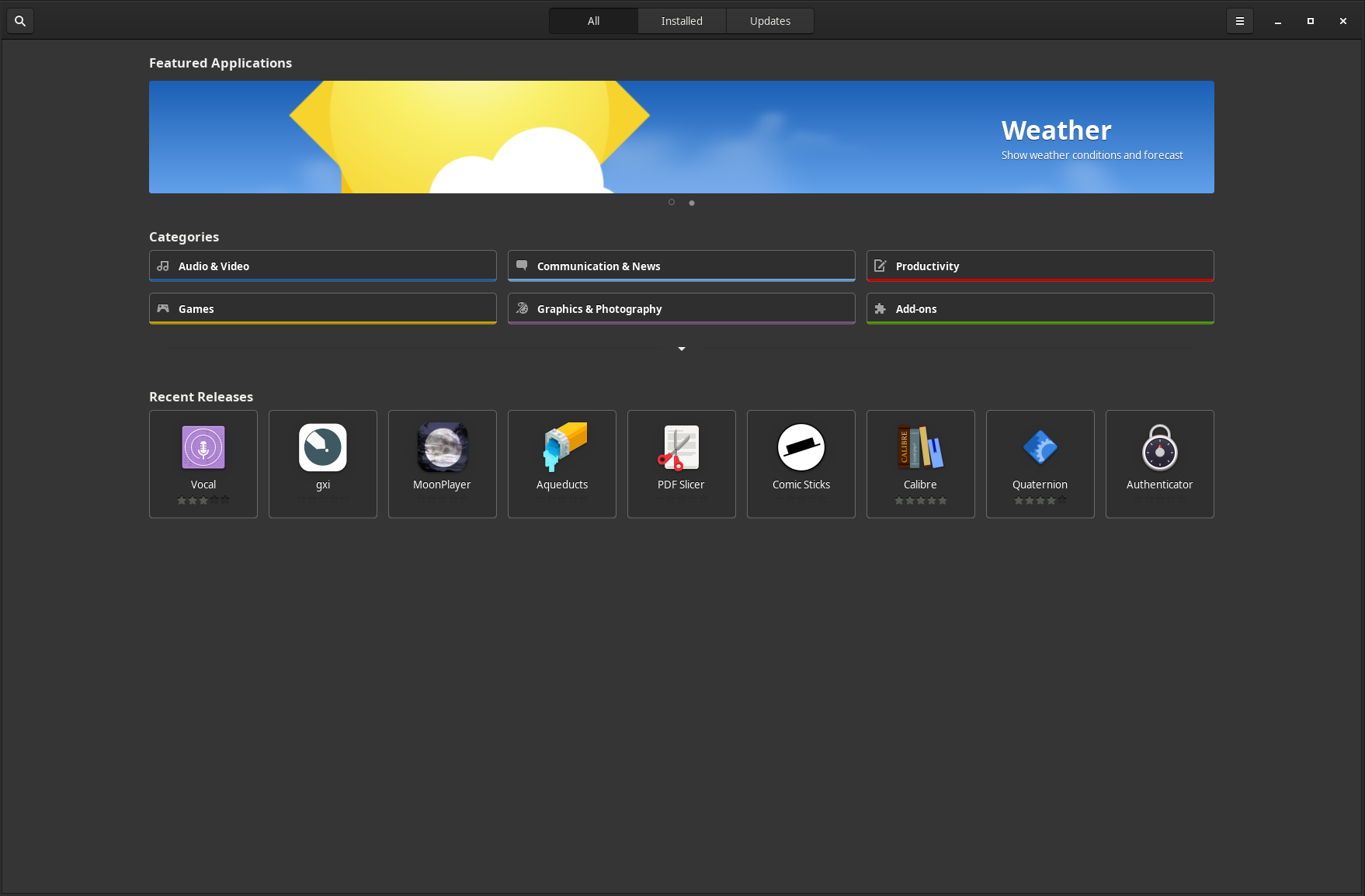
Managing Flatpaks via Gnome Software
One way to manage your Flatpaks is with the application Gnome Software from the Gnome project. You can install the package gnome-software with your favorite package manager or the command:
pamac install gnome-software
Once installed you can run Software and you will be able to browse, install and update Flatpaks with a familiar store interface.
Managing Flatpaks via the CLI
Finding and Installing Flatpaks
You can use the command flatpak search to search for available Flatpaks. For example, if you wanted to install VLC here is what it might look like:
flatpak search vlc Name Description Application ID Version Branch Remotes MakeMKV plugin for VLC Provides MakeMKV features for direct Blu-ray playback in VLC. org.videolan.VLC.Plugin.makemkv 3-18.08 flathub Bluray Java menus (BDJ) plugin for VLC Provides Bluray Java menus (BDJ) support in VLC. org.videolan.VLC.Plugin.bdj 3-18.08 flathub VLC VLC media player, the open-source multimedia player org.videolan.VLC stable flathub FDK-AAC Encoding Plugin for VLC Provides better AAC encoding and HE profiles support. org.videolan.VLC.Plugin.fdkaac 3-1.6 flathub
From this output we can see that VLC and some related applications via Flatpak. To install VLC, we would use it's "Application ID", shown above with the command
flatpak install org.videolan.VLC
This will install the application as well as any required run-times. Once the application is installed you should be able to run it from your menu as you would with any application.
Displaying Detailed Flatpak Information
You can get more details about a specific Flatpak using the command flatpak info. For example:
flatpak info org.videolan.VLC
VLC - VLC media player, the open-source multimedia player
ID: org.videolan.VLC
Ref: app/org.videolan.VLC/x86_64/stable
Arch: x86_64
Branch: stable
License: GPL-2.0+
Origin: flathub
Collection: org.flathub.Stable
Installation: system
Installed: 81.4 MB
Runtime: org.kde.Platform/x86_64/5.12
Sdk: org.kde.Sdk/x86_64/5.12
Commit: 87a8e23cefe6c3f4962d303d3724db399872e68379a52b7553089f5540c9a883
Parent: 8f0c0e0bd79bfeb8748bb53e8476ee1f2deffc0e131ea5fb2890505e449df8a2
Subject: Update shared-modules for udev (d3f66ebc)
Date: 2019-05-06 13:30:44 +0000
Getting installed Flatpaks
To show a list of all the Flatpaks and run-times that are currently installed you can use the command:
flatpak list
Updating Flatpaks
Updating your collection of Flatpaks is a simple process. Simply run the command:
flatpak upgrade
Removing Flatpaks
You can remove Flatpaks with the command flatpak uninstall. For example:
flatpak uninstall org.videolan.VLC
Removing Flatpak Support
If you no longer wish to have support for the Flatpack in your system you can remove it from the system by simply removing the package flatpak with your favorite package manager or with the command
pamac remove flatpak
To also remove any installed Flatpaks you need to remove the directories containing them. These are /var/lib/flatpak and ~/.local/share/flatpak. For example, you could use the command
sudo rm -r /var/lib/flatpak rm -r ~/.local/share/flatpak