Difference between revisions of "Power Management"
Views
Actions
Namespaces
Variants
Tools
imported>Aaditya (Created page with " Power Saving Techniques can be used on Laptops to maximize the Battery Life and minimize the heat produced, and conserve energy. == Power Saving using TLP == TLP can be use...") |
(Marked this version for translation) |
||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages/> | |||
__TOC__ | |||
Power Saving | <translate> | ||
<!--T:1--> | |||
Power Saving techniques can be used to minimize the heat produced and conserve energy. On laptops, this can be especially important as it can significantly extend battery life and excessive heat can be both uncomfortable and loud on portable devices. | |||
=Power Management Software= <!--T:2--> | |||
[[File:battery.png|left|96px]] | |||
< | <!--T:3--> | ||
There are several options for managing power under Manjaro. In this article, we will introduce three of the more popular options. | |||
<!--T:4--> | |||
{{note|In most cases running more than one power management tool at a time can cause conflicts so it is best practice to only use one of the below options}} | |||
<!--T:5--> | |||
<br clear="all"/> | |||
== | ==TLP== <!--T:6--> | ||
TLP is | <!--T:7--> | ||
[http://linrunner.de/en/tlp/tlp.html TLP] is the most commonly used option for automatic power management. | |||
===Installing TLP=== <!--T:8--> | |||
<!--T:9--> | |||
TLP is available from the Manjaro repositories, can be installed with your favorite package manager or by using entering the following command into your terminal: | |||
<!--T:10--> | |||
pamac install tlp | |||
<!--T:11--> | |||
Now that it is installed, you need to start and enable the service. This can be accomplished with the command: | |||
systemctl enable tlp --now | |||
<!--T:12--> | |||
{{note|TLP 1.2.2 and lower need another service as well: tlp-sleep.service}} | |||
== | ===Configuring TLP=== <!--T:13--> | ||
[[File:Tlpui.png|left|400px]] | |||
< | <!--T:14--> | ||
TLP can manually configured by editing the file '''/etc/default/tlp''' as described in [http://linrunner.de/en/tlp/docs/tlp-configuration.html The Official Documentation]. | |||
<!--T:15--> | |||
A simpler way to configure TLP is via the GUI tool [https://github.com/d4nj1/TLPUI TLPUI] | |||
<!--T:16--> | |||
To install TLPUI install the package '''tlpui''' using your favorite package manager or with the command | |||
pamac install tlpui | |||
<!--T:17--> | |||
<br clear="all"/> | |||
==Laptop Mode Tools== <!--T:18--> | |||
<!--T:19--> | |||
An Alternative to TLP for laptops is [https://github.com/rickysarraf/laptop-mode-tools Laptop Mode Tools(LMT)]. | |||
===Installing LMT=== <!--T:20--> | |||
<!--T:21--> | |||
To install {{ic|laptop-mode-tools}}, enter the following command into your terminal: | |||
<!--T:22--> | |||
pamac install laptop-mode-tools | |||
<!--T:23--> | |||
Once installed, to enable LMT to start automatically every time you boot your computer, enter the following into your terminal: | |||
<!--T:24--> | |||
sudo systemctl enable --now laptop-mode.service | |||
<!--T:25--> | |||
LMT automatically configures some settings for you in order to optimize your laptop's battery life. | |||
===LMT Configuration=== <!--T:26--> | |||
<!--T:27--> | |||
For configuration, the file to edit is {{ic|/etc/laptop-mode/laptop-mode.conf}}} | |||
<!--T:28--> | |||
The individual kernel modules can be configured from the configuration files present in {{ic|/etc/laptop-mode/conf.d/}} | |||
==PowerTOP== <!--T:29--> | |||
<!--T:30--> | |||
PowerTop a diagnostic tool used to identify and report issues with power consumption and management. It can be used as a reporting tool, an automated power management tool or both. | |||
===Installing PowerTop=== <!--T:31--> | |||
<!--T:32--> | |||
It can be installed as | |||
pamac install powertop | |||
== | ===Generating Reports=== <!--T:33--> | ||
<!--T:34--> | |||
You can generate a report using powertop with the command: | |||
sudo powertop --html | |||
sudo | |||
<!--T:35--> | |||
This will create the file {{ic|powertop.html}} in the current directory. You can open this file in any web browser. | |||
<!--T:36--> | |||
If you are using TLP for power management you may notice some differences in the recommendations between the tools. The article [http://linrunner.de/en/tlp/docs/tlp-faq.html#powertop Comparing TLP with PowerTop reporting] describes some of the reasons for these differences. | |||
= | ===Automated Tuning with PowerTop=== <!--T:37--> | ||
<!--T:38--> | |||
The command {{ic|sudo powertop --auto-tune"}} will allow PowerTop to automatically tune power management based on it's recommendations. | |||
<!--T:39--> | |||
From a practical perspective, the best way to use PowerTops auto-tuning is with a systemd service. | |||
<!--T:40--> | |||
To create, start and enable a systemd service for PowerTop you can use the commands: | |||
sudo sh -c "echo -e '[Unit]\nDescription=PowerTop\n\n[Service]\nType=oneshot\nRemainAfterExit=true\nExecStart=/usr/bin/powertop --auto-tune\n\n[Install]\nWantedBy=multi-user.target\n' > /etc/systemd/system/powertop.service" | |||
sudo systemctl enable --now powertop.service | |||
=Temperature/Thermal Management= <!--T:41--> | |||
= | ==ThermalD== <!--T:42--> | ||
[https://github.com/intel/thermal_daemon ThermalD], the Linux Thermal Daemon can be used to automatically handle CPU frequency scaling according to system load. | |||
<!--T:43--> | |||
To install it, install {{ic|thermald}} in your favorite package manager or use the command: | |||
pamac install thermald | |||
<!--T:44--> | |||
After installing it needs to be configured to automatically start at boot in order to work: | |||
sudo systemctl enable --now thermald | |||
[https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Laptop_Mode_Tools LaptopModeTools-Arch Wiki] | </translate> | ||
<translate> | |||
=See Also= <!--T:45--> | |||
* [[Undervolt_intel_CPU|How to undervolt Intel CPUs]] | |||
* [http://linrunner.de/en/tlp/tlp.html TLP website] | |||
* [https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Laptop_Mode_Tools LaptopModeTools - Arch Wiki] | |||
* [https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/TLP TLP - Arch wiki] | |||
</translate> | |||
[[Category:Contents Page]] | [[Category:Contents Page{{#translation:}}]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:58, 23 January 2023
Power Saving techniques can be used to minimize the heat produced and conserve energy. On laptops, this can be especially important as it can significantly extend battery life and excessive heat can be both uncomfortable and loud on portable devices.
Power Management Software
There are several options for managing power under Manjaro. In this article, we will introduce three of the more popular options.
TLP
TLP is the most commonly used option for automatic power management.
Installing TLP
TLP is available from the Manjaro repositories, can be installed with your favorite package manager or by using entering the following command into your terminal:
pamac install tlp
Now that it is installed, you need to start and enable the service. This can be accomplished with the command:
systemctl enable tlp --now
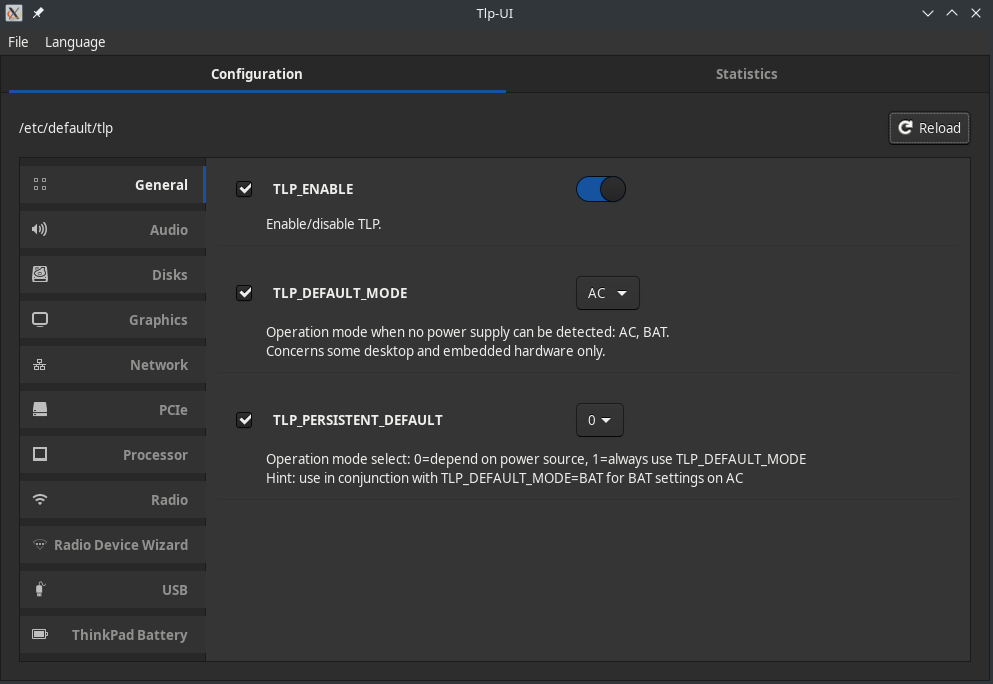
Configuring TLP
TLP can manually configured by editing the file /etc/default/tlp as described in The Official Documentation.
A simpler way to configure TLP is via the GUI tool TLPUI
To install TLPUI install the package tlpui using your favorite package manager or with the command
pamac install tlpui
Laptop Mode Tools
An Alternative to TLP for laptops is Laptop Mode Tools(LMT).
Installing LMT
To install laptop-mode-tools, enter the following command into your terminal:
pamac install laptop-mode-tools
Once installed, to enable LMT to start automatically every time you boot your computer, enter the following into your terminal:
sudo systemctl enable --now laptop-mode.service
LMT automatically configures some settings for you in order to optimize your laptop's battery life.
LMT Configuration
For configuration, the file to edit is /etc/laptop-mode/laptop-mode.conf}
The individual kernel modules can be configured from the configuration files present in /etc/laptop-mode/conf.d/
PowerTOP
PowerTop a diagnostic tool used to identify and report issues with power consumption and management. It can be used as a reporting tool, an automated power management tool or both.
Installing PowerTop
It can be installed as
pamac install powertop
Generating Reports
You can generate a report using powertop with the command:
sudo powertop --html
This will create the file powertop.html in the current directory. You can open this file in any web browser.
If you are using TLP for power management you may notice some differences in the recommendations between the tools. The article Comparing TLP with PowerTop reporting describes some of the reasons for these differences.
Automated Tuning with PowerTop
The command sudo powertop --auto-tune" will allow PowerTop to automatically tune power management based on it's recommendations.
From a practical perspective, the best way to use PowerTops auto-tuning is with a systemd service.
To create, start and enable a systemd service for PowerTop you can use the commands:
sudo sh -c "echo -e '[Unit]\nDescription=PowerTop\n\n[Service]\nType=oneshot\nRemainAfterExit=true\nExecStart=/usr/bin/powertop --auto-tune\n\n[Install]\nWantedBy=multi-user.target\n' > /etc/systemd/system/powertop.service" sudo systemctl enable --now powertop.service
Temperature/Thermal Management
ThermalD
ThermalD, the Linux Thermal Daemon can be used to automatically handle CPU frequency scaling according to system load.
To install it, install thermald in your favorite package manager or use the command:
pamac install thermald
After installing it needs to be configured to automatically start at boot in order to work:
sudo systemctl enable --now thermald