Difference between revisions of "Power Management/zh-cn"
Views
Actions
Namespaces
Variants
Tools
(Created page with "Manjaro有多款电源管理软件可供选择,以下介绍几款流行的软件。") |
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
{{note|通常情况下,应该只选择一款电源管理软件来管理功耗,避免因为安装过多的功耗管理工具导致冲突,甚至是适得其反}} | {{note|通常情况下,应该只选择一款电源管理软件来管理功耗,避免因为安装过多的功耗管理工具导致冲突,甚至是适得其反}} | ||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
<br clear="all"/> | <br clear="all"/> | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
==TLP== | ==TLP== | ||
</div> | |||
[http://linrunner.de/en/tlp/tlp.html TLP]是自动化电源管理的最常用方案 | [http://linrunner.de/en/tlp/tlp.html TLP]是自动化电源管理的最常用方案 | ||
| Line 25: | Line 29: | ||
TLP可以直接从Manjaro的存储库中获得,也可以使用其他包管理器或者终端命令方式安装 | TLP可以直接从Manjaro的存储库中获得,也可以使用其他包管理器或者终端命令方式安装 | ||
pamac install tlp | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
pamac install tlp | |||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
Now that it is installed, you need to start and enable the service. This can be accomplished with the command: | Now that it is installed, you need to start and enable the service. This can be accomplished with the command: | ||
systemctl enable tlp --now | systemctl enable tlp --now | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
{{note|TLP 1.2.2 and lower need another service as well: tlp-sleep.service}} | {{note|TLP 1.2.2 and lower need another service as well: tlp-sleep.service}} | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
===Configuring TLP=== | ===Configuring TLP=== | ||
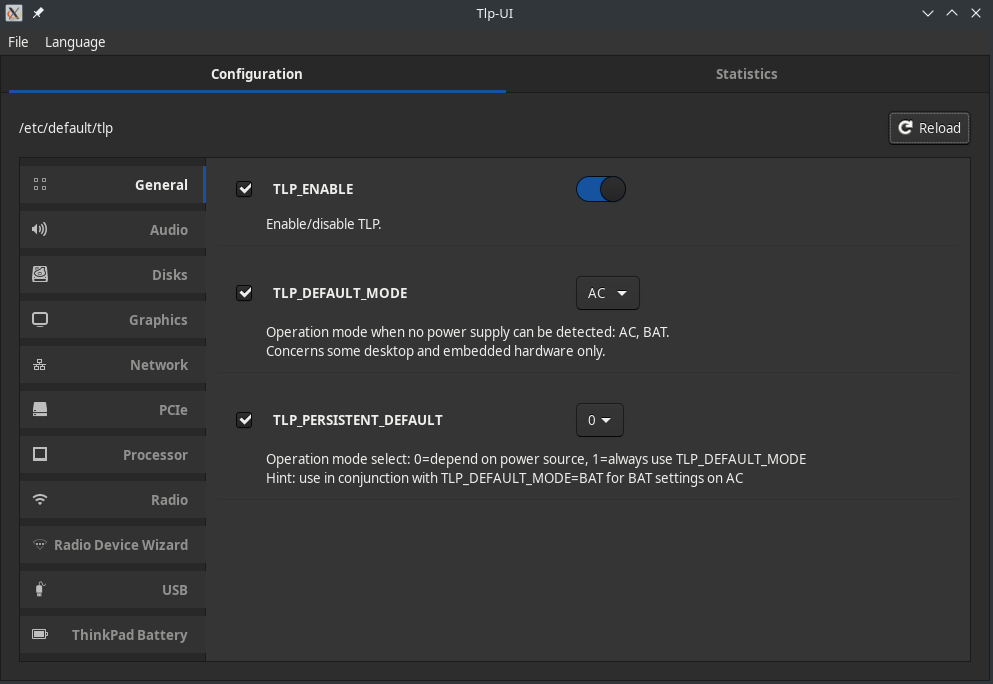
[[File:Tlpui.png|left|400px]] | [[File:Tlpui.png|left|400px]] | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
TLP can manually configured by editing the file '''/etc/default/tlp''' as described in [http://linrunner.de/en/tlp/docs/tlp-configuration.html The Official Documentation]. | TLP can manually configured by editing the file '''/etc/default/tlp''' as described in [http://linrunner.de/en/tlp/docs/tlp-configuration.html The Official Documentation]. | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
A simpler way to configure TLP is via the GUI tool [https://github.com/d4nj1/TLPUI TLPUI] | A simpler way to configure TLP is via the GUI tool [https://github.com/d4nj1/TLPUI TLPUI] | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
To install TLPUI install the package '''tlpui''' using your favorite package manager or with the command | To install TLPUI install the package '''tlpui''' using your favorite package manager or with the command | ||
pamac install tlpui | pamac install tlpui | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
<br clear="all"/> | <br clear="all"/> | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
==Laptop Mode Tools== | ==Laptop Mode Tools== | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
An Alternative to TLP for laptops is [https://github.com/rickysarraf/laptop-mode-tools Laptop Mode Tools(LMT)]. | An Alternative to TLP for laptops is [https://github.com/rickysarraf/laptop-mode-tools Laptop Mode Tools(LMT)]. | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
===Installing LMT=== | ===Installing LMT=== | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
To install {{ic|laptop-mode-tools}}, enter the following command into your terminal: | To install {{ic|laptop-mode-tools}}, enter the following command into your terminal: | ||
</div> | |||
pamac install laptop-mode-tools | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
pamac install laptop-mode-tools | |||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
Once installed, to enable LMT to start automatically every time you boot your computer, enter the following into your terminal: | Once installed, to enable LMT to start automatically every time you boot your computer, enter the following into your terminal: | ||
</div> | |||
sudo systemctl enable --now laptop-mode.service | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
sudo systemctl enable --now laptop-mode.service | |||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
LMT automatically configures some settings for you in order to optimize your laptop's battery life. | LMT automatically configures some settings for you in order to optimize your laptop's battery life. | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
===LMT Configuration=== | ===LMT Configuration=== | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
For configuration, the file to edit is {{ic|/etc/laptop-mode/laptop-mode.conf}}} | For configuration, the file to edit is {{ic|/etc/laptop-mode/laptop-mode.conf}}} | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
The individual kernel modules can be configured from the configuration files present in {{ic|/etc/laptop-mode/conf.d/}} | The individual kernel modules can be configured from the configuration files present in {{ic|/etc/laptop-mode/conf.d/}} | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
==PowerTOP== | ==PowerTOP== | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
PowerTop a diagnostic tool used to identify and report issues with power consumption and management. It can be used as a reporting tool, an automated power management tool or both. | PowerTop a diagnostic tool used to identify and report issues with power consumption and management. It can be used as a reporting tool, an automated power management tool or both. | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
===Installing PowerTop=== | ===Installing PowerTop=== | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
It can be installed as | It can be installed as | ||
pamac install powertop | pamac install powertop | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
===Generating Reports=== | ===Generating Reports=== | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
You can generate a report using powertop with the command: | You can generate a report using powertop with the command: | ||
sudo powertop --html | sudo powertop --html | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
This will create the file {{ic|powertop.html}} in the current directory. You can open this file in any web browser. | This will create the file {{ic|powertop.html}} in the current directory. You can open this file in any web browser. | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
If you are using TLP for power management you may notice some differences in the recommendations between the tools. The article [http://linrunner.de/en/tlp/docs/tlp-faq.html#powertop Comparing TLP with PowerTop reporting] describes some of the reasons for these differences. | If you are using TLP for power management you may notice some differences in the recommendations between the tools. The article [http://linrunner.de/en/tlp/docs/tlp-faq.html#powertop Comparing TLP with PowerTop reporting] describes some of the reasons for these differences. | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
===Automated Tuning with PowerTop=== | ===Automated Tuning with PowerTop=== | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
The command {{ic|sudo powertop --auto-tune"}} will allow PowerTop to automatically tune power management based on it's recommendations. | The command {{ic|sudo powertop --auto-tune"}} will allow PowerTop to automatically tune power management based on it's recommendations. | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
From a practical perspective, the best way to use PowerTops auto-tuning is with a systemd service. | From a practical perspective, the best way to use PowerTops auto-tuning is with a systemd service. | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
To create, start and enable a systemd service for PowerTop you can use the commands: | To create, start and enable a systemd service for PowerTop you can use the commands: | ||
sudo sh -c "echo -e '[Unit]\nDescription=PowerTop\n\n[Service]\nType=oneshot\nRemainAfterExit=true\nExecStart=/usr/bin/powertop --auto-tune\n\n[Install]\nWantedBy=multi-user.target\n' > /etc/systemd/system/powertop.service" | sudo sh -c "echo -e '[Unit]\nDescription=PowerTop\n\n[Service]\nType=oneshot\nRemainAfterExit=true\nExecStart=/usr/bin/powertop --auto-tune\n\n[Install]\nWantedBy=multi-user.target\n' > /etc/systemd/system/powertop.service" | ||
sudo systemctl enable --now powertop.service | sudo systemctl enable --now powertop.service | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
=Temperature/Thermal Management= | =Temperature/Thermal Management= | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
==ThermalD== | ==ThermalD== | ||
[https://github.com/intel/thermal_daemon ThermalD], the Linux Thermal Daemon can be used to automatically handle CPU frequency scaling according to system load. | [https://github.com/intel/thermal_daemon ThermalD], the Linux Thermal Daemon can be used to automatically handle CPU frequency scaling according to system load. | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
To install it, install {{ic|thermald}} in your favorite package manager or use the command: | To install it, install {{ic|thermald}} in your favorite package manager or use the command: | ||
pamac install thermald | pamac install thermald | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
After installing it needs to be configured to automatically start at boot in order to work: | After installing it needs to be configured to automatically start at boot in order to work: | ||
sudo systemctl enable --now thermald | sudo systemctl enable --now thermald | ||
</div> | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
=See Also= | =See Also= | ||
* [[Undervolt_intel_CPU|How to undervolt Intel CPUs]] | * [[Undervolt_intel_CPU|How to undervolt Intel CPUs]] | ||
| Line 121: | Line 196: | ||
* [https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Laptop_Mode_Tools LaptopModeTools - Arch Wiki] | * [https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Laptop_Mode_Tools LaptopModeTools - Arch Wiki] | ||
* [https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/TLP TLP - Arch wiki] | * [https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/TLP TLP - Arch wiki] | ||
</div> | |||
[[Category:Contents Page{{#translation:}}]] | [[Category:Contents Page{{#translation:}}]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:58, 23 January 2023
有效的电源管理可以帮助设备降低发热并且省电,在笔记本电脑上这点体现的更加明显,因为它还可以延长笔记本电池的使用寿命,让你免除设备风扇的操作和键盘本身发热带来的不适
电源管理软件
Manjaro有多款电源管理软件可供选择,以下介绍几款流行的软件。
TLP
TLP是自动化电源管理的最常用方案
安装 TLP
TLP可以直接从Manjaro的存储库中获得,也可以使用其他包管理器或者终端命令方式安装
pamac install tlp
Now that it is installed, you need to start and enable the service. This can be accomplished with the command:
systemctl enable tlp --now
TLP can manually configured by editing the file /etc/default/tlp as described in The Official Documentation.
A simpler way to configure TLP is via the GUI tool TLPUI
To install TLPUI install the package tlpui using your favorite package manager or with the command
pamac install tlpui
Laptop Mode Tools
An Alternative to TLP for laptops is Laptop Mode Tools(LMT).
Installing LMT
To install laptop-mode-tools, enter the following command into your terminal:
pamac install laptop-mode-tools
Once installed, to enable LMT to start automatically every time you boot your computer, enter the following into your terminal:
sudo systemctl enable --now laptop-mode.service
LMT automatically configures some settings for you in order to optimize your laptop's battery life.
LMT Configuration
For configuration, the file to edit is /etc/laptop-mode/laptop-mode.conf}
The individual kernel modules can be configured from the configuration files present in /etc/laptop-mode/conf.d/
PowerTOP
PowerTop a diagnostic tool used to identify and report issues with power consumption and management. It can be used as a reporting tool, an automated power management tool or both.
Installing PowerTop
It can be installed as
pamac install powertop
Generating Reports
You can generate a report using powertop with the command:
sudo powertop --html
This will create the file powertop.html in the current directory. You can open this file in any web browser.
If you are using TLP for power management you may notice some differences in the recommendations between the tools. The article Comparing TLP with PowerTop reporting describes some of the reasons for these differences.
Automated Tuning with PowerTop
The command sudo powertop --auto-tune" will allow PowerTop to automatically tune power management based on it's recommendations.
From a practical perspective, the best way to use PowerTops auto-tuning is with a systemd service.
To create, start and enable a systemd service for PowerTop you can use the commands:
sudo sh -c "echo -e '[Unit]\nDescription=PowerTop\n\n[Service]\nType=oneshot\nRemainAfterExit=true\nExecStart=/usr/bin/powertop --auto-tune\n\n[Install]\nWantedBy=multi-user.target\n' > /etc/systemd/system/powertop.service" sudo systemctl enable --now powertop.service
Temperature/Thermal Management
ThermalD
ThermalD, the Linux Thermal Daemon can be used to automatically handle CPU frequency scaling according to system load.
To install it, install thermald in your favorite package manager or use the command:
pamac install thermald
After installing it needs to be configured to automatically start at boot in order to work:
sudo systemctl enable --now thermald